Tech
EXW Incoterms Simplified for Buyers and Sellers (2026)
Understanding EXW Incoterms is essential for anyone involved in international trade in 2026. Ex Works (EXW) is a shipping arrangement where the seller makes goods available at a designated location, and the buyer covers transport costs, including loading, shipping, customs export fees, and insurance. Unlike FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), EXW places almost all responsibilities and risk transfer on the buyer. Sellers are only responsible for packing, labeling, and providing the pickup point. Knowing how EXW compares with other Incoterms, such as DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) or FCA (Free Carrier), helps businesses make informed decisions, avoid hidden costs, and streamline shipping and customs documentation effectively.
What Is Ex Works (EXW)?
Ex Works (EXW) is one of the 11 Incoterms used in international trade. Under EXW, the seller simply makes goods available at a designated location, often their warehouse or factory. The buyer then covers all transportation costs, loading and unloading, and any customs-related fees.
Think of EXW like buying from a store and carrying everything home yourself. You handle risk transfer, shipping, and all responsibilities after the seller makes the goods ready. Sellers have minimal obligations, making EXW a low-cost option for them but a high-responsibility choice for buyers.
Understanding Ex Works (EXW)
With EXW, the seller’s duty is mainly packing and labeling the goods correctly. They must provide a safe location for the buyer to pick up products. If export licenses are needed, the seller assists but does not pay for them.
Buyers, on the other hand, take on almost all costs and responsibilities. This includes:
- Loading products onto trucks
- Transporting to ports or shipping terminals
- Paying for customs export fees
- Arranging sea or air freight
- Insurance from pickup point onward
- Unloading at the destination
This arrangement makes EXW less expensive for sellers but places significant responsibility on buyers. It works best if the buyer has a local representative in the seller’s country.
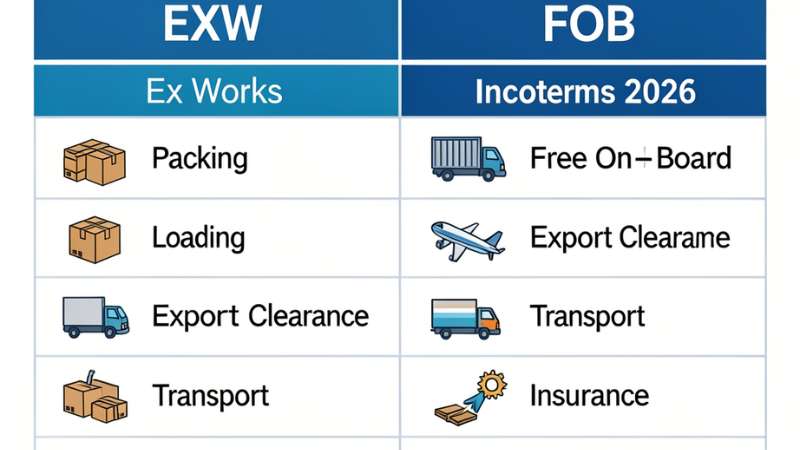
Ex Works vs. FOB
EXW and FOB (Free On Board) differ in responsibilities and risk transfer. With FOB, the seller delivers goods to the port and loads them on the vessel. They also handle export customs documentation. Risk passes to the buyer once goods are on the ship.
| Feature | EXW | FOB |
|---|---|---|
| Seller responsibility | Minimal; packing & location | Packing, transport to port, loading, customs |
| Buyer responsibility | All transport, customs, insurance | Shipping, customs at destination, insurance |
| Risk transfer | When goods are made available | When goods are on board the vessel |
| Cost to buyer | Higher | Moderate |
| Best for | Experienced buyers | Buyers wanting partial seller support |
FOB is generally safer for buyers unfamiliar with exporting rules, whereas EXW is better for buyers who can manage logistics efficiently.
Responsibilities Under Ex Works
Buyer responsibilities under EXW include:
- Paying loading charges at pickup point
- Transporting goods to port or destination
- Covering customs export and import fees
- Arranging shipping, insurance, and unloading
Seller responsibilities are limited:
- Correctly pack and label goods
- Provide a pickup location
- Assist with export documents if required
This clear division ensures everyone knows their role in international trade contracts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ex Works
Advantages:
- Low cost for sellers – minimal obligations
- Easy to purchase in domestic markets
- Helps buyers consolidate multiple purchases
- Can anonymize suppliers from competitors
Disadvantages:
- Buyers bear all risk after pickup
- Requires a trusted local representative
- Costs may exceed expectations if unfamiliar with shipping
- Not ideal for first-time international buyers
Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide if EXW fits your business needs.
Incoterms
Incoterms are rules defined by the International Chamber of Commerce to standardize trade. They clarify:
- When risk transfer occurs
- Who pays for freight and insurance
- Delivery and payment points
There are 11 main Incoterms:
- EXW – Ex Works
- FCA – Free Carrier
- CPT – Carriage Paid To
- CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid To
- DAP – Delivered at Place
- DPU – Delivered at Place Unloaded
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship
- FOB – Free On Board
- CFR – Cost and Freight
- CIF – Cost, Insurance, and Freight
Each term defines the division of costs, responsibilities, and risks for sellers and buyers.
What Does Ex Works Mean in Incoterms?
In Incoterms, EXW means the seller’s responsibility ends once goods are ready for pickup. Buyers take on the risk and cost of transport from that point onward.
This includes:
- Arranging shipping via truck, ship, or plane
- Paying insurance and customs fees
- Managing destination delivery
Essentially, the buyer assumes control over logistics and liability as soon as goods are made available.
What Is the Difference Between Ex Works and FOB?
The main difference lies in seller involvement and risk transfer:
- EXW – Seller’s job is minimal; risk passes at pickup location
- FOB – Seller delivers to port and loads; risk passes on ship
Example: If goods are damaged during loading at port:
- Under EXW, the buyer bears the cost
- Under FOB, the seller is responsible until the goods are on board
Understanding this helps buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Does Ex Works Mean for Shipping?
With EXW, the buyer controls:
- Choice of shipping method
- Coordination with freight forwarders
- Storage and unloading at the destination
Sellers only ensure goods are available and labeled correctly. It’s like picking up a package and handling the rest yourself.
How Does Insurance Work With Ex Works Terms?
Insurance under EXW is entirely the buyer’s responsibility. Since risk transfers to the buyer once goods are made available, the buyer should:
- Arrange coverage from pickup point onward
- Include loading, shipping, and unloading risks
- Verify coverage in case of customs delays or accidents
Without insurance, buyers could face significant losses.
Who Arranges Customs Documentation in Ex Works?
Under EXW, buyers handle all customs documentation:
- Export licenses from the seller’s country
- Import permits in the destination country
- Filing necessary forms for tariffs and duties
Sellers may assist in paperwork, but buyers must pay fees and ensure compliance.
Related Articals:
Robotic and automation in 2026
Top AI Stock under $10 to buy in 2026
Conclusion:
EXW Incoterms give sellers minimal responsibility but place all logistics, risk, and costs on buyers. It’s best for buyers who are experienced, have local representatives, or wish to consolidate shipments. Comparing EXW with FOB and other Incoterms helps businesses choose the right shipping agreement. Always consider risk transfer, customs requirements, and insurance to avoid unexpected costs.
By understanding EXW, buyers and sellers can make informed decisions, save costs, and ensure smooth international trade.
References
FAQ
1. What does EXW mean in shipping terms?
EXW (Ex Works) means the seller makes goods available at a specific location, and the buyer is responsible for all transport and related risks from that point onward.
2. Who pays for shipping under EXW?
The buyer pays for all shipping costs, including transport to the port, freight, customs duties, and insurance. The seller only prepares and packages the goods.
3. What is the difference between FOB and EXW?
Under FOB, the seller delivers goods to the port and loads them on the ship, handling export clearance. Under EXW, the seller’s responsibility ends at their premises, and the buyer handles everything after pickup.
4. What are the Incoterms of Ex Works?
EXW is one of the 11 main Incoterms by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining minimal seller responsibility and maximum buyer responsibility. It standardizes delivery, cost, and risk transfer.
5. Who is responsible in EXW?
The buyer is responsible for all transportation, customs, insurance, and delivery costs. The seller only ensures goods are packed, labeled, and ready for pickup.