Tech
EXW Incoterms Simplified for Buyers and Sellers (2026)

Understanding EXW Incoterms is essential for anyone involved in international trade in 2026. Ex Works (EXW) is a shipping arrangement where the seller makes goods available at a designated location, and the buyer covers transport costs, including loading, shipping, customs export fees, and insurance. Unlike FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), EXW places almost all responsibilities and risk transfer on the buyer. Sellers are only responsible for packing, labeling, and providing the pickup point. Knowing how EXW compares with other Incoterms, such as DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) or FCA (Free Carrier), helps businesses make informed decisions, avoid hidden costs, and streamline shipping and customs documentation effectively.
What Is Ex Works (EXW)?
Ex Works (EXW) is one of the 11 Incoterms used in international trade. Under EXW, the seller simply makes goods available at a designated location, often their warehouse or factory. The buyer then covers all transportation costs, loading and unloading, and any customs-related fees.
Think of EXW like buying from a store and carrying everything home yourself. You handle risk transfer, shipping, and all responsibilities after the seller makes the goods ready. Sellers have minimal obligations, making EXW a low-cost option for them but a high-responsibility choice for buyers.
Understanding Ex Works (EXW)
With EXW, the seller’s duty is mainly packing and labeling the goods correctly. They must provide a safe location for the buyer to pick up products. If export licenses are needed, the seller assists but does not pay for them.
Buyers, on the other hand, take on almost all costs and responsibilities. This includes:
- Loading products onto trucks
- Transporting to ports or shipping terminals
- Paying for customs export fees
- Arranging sea or air freight
- Insurance from pickup point onward
- Unloading at the destination
This arrangement makes EXW less expensive for sellers but places significant responsibility on buyers. It works best if the buyer has a local representative in the seller’s country.
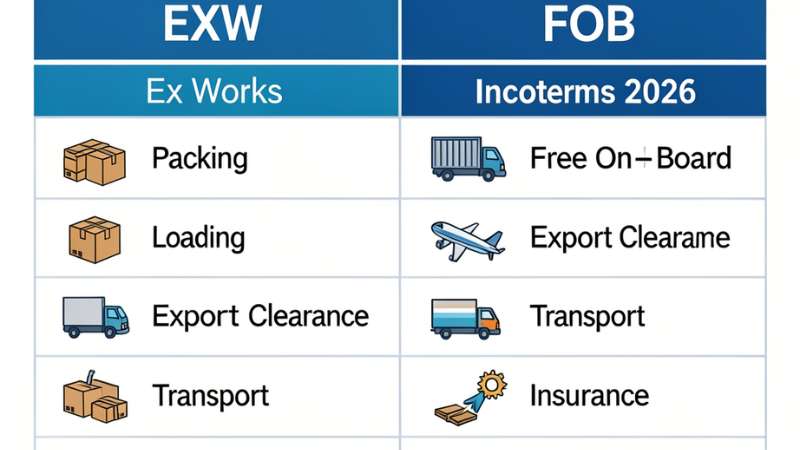
Ex Works vs. FOB
EXW and FOB (Free On Board) differ in responsibilities and risk transfer. With FOB, the seller delivers goods to the port and loads them on the vessel. They also handle export customs documentation. Risk passes to the buyer once goods are on the ship.
| Feature | EXW | FOB |
|---|---|---|
| Seller responsibility | Minimal; packing & location | Packing, transport to port, loading, customs |
| Buyer responsibility | All transport, customs, insurance | Shipping, customs at destination, insurance |
| Risk transfer | When goods are made available | When goods are on board the vessel |
| Cost to buyer | Higher | Moderate |
| Best for | Experienced buyers | Buyers wanting partial seller support |
FOB is generally safer for buyers unfamiliar with exporting rules, whereas EXW is better for buyers who can manage logistics efficiently.
Responsibilities Under Ex Works
Buyer responsibilities under EXW include:
- Paying loading charges at pickup point
- Transporting goods to port or destination
- Covering customs export and import fees
- Arranging shipping, insurance, and unloading
Seller responsibilities are limited:
- Correctly pack and label goods
- Provide a pickup location
- Assist with export documents if required
This clear division ensures everyone knows their role in international trade contracts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ex Works
Advantages:
- Low cost for sellers – minimal obligations
- Easy to purchase in domestic markets
- Helps buyers consolidate multiple purchases
- Can anonymize suppliers from competitors
Disadvantages:
- Buyers bear all risk after pickup
- Requires a trusted local representative
- Costs may exceed expectations if unfamiliar with shipping
- Not ideal for first-time international buyers
Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide if EXW fits your business needs.
Incoterms
Incoterms are rules defined by the International Chamber of Commerce to standardize trade. They clarify:
- When risk transfer occurs
- Who pays for freight and insurance
- Delivery and payment points
There are 11 main Incoterms:
- EXW – Ex Works
- FCA – Free Carrier
- CPT – Carriage Paid To
- CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid To
- DAP – Delivered at Place
- DPU – Delivered at Place Unloaded
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship
- FOB – Free On Board
- CFR – Cost and Freight
- CIF – Cost, Insurance, and Freight
Each term defines the division of costs, responsibilities, and risks for sellers and buyers.
What Does Ex Works Mean in Incoterms?
In Incoterms, EXW means the seller’s responsibility ends once goods are ready for pickup. Buyers take on the risk and cost of transport from that point onward.
This includes:
- Arranging shipping via truck, ship, or plane
- Paying insurance and customs fees
- Managing destination delivery
Essentially, the buyer assumes control over logistics and liability as soon as goods are made available.
What Is the Difference Between Ex Works and FOB?
The main difference lies in seller involvement and risk transfer:
- EXW – Seller’s job is minimal; risk passes at pickup location
- FOB – Seller delivers to port and loads; risk passes on ship
Example: If goods are damaged during loading at port:
- Under EXW, the buyer bears the cost
- Under FOB, the seller is responsible until the goods are on board
Understanding this helps buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
What Does Ex Works Mean for Shipping?
With EXW, the buyer controls:
- Choice of shipping method
- Coordination with freight forwarders
- Storage and unloading at the destination
Sellers only ensure goods are available and labeled correctly. It’s like picking up a package and handling the rest yourself.
How Does Insurance Work With Ex Works Terms?
Insurance under EXW is entirely the buyer’s responsibility. Since risk transfers to the buyer once goods are made available, the buyer should:
- Arrange coverage from pickup point onward
- Include loading, shipping, and unloading risks
- Verify coverage in case of customs delays or accidents
Without insurance, buyers could face significant losses.
Who Arranges Customs Documentation in Ex Works?
Under EXW, buyers handle all customs documentation:
- Export licenses from the seller’s country
- Import permits in the destination country
- Filing necessary forms for tariffs and duties
Sellers may assist in paperwork, but buyers must pay fees and ensure compliance.
Related Articals:
Robotic and automation in 2026
Top AI Stock under $10 to buy in 2026
Conclusion:
EXW Incoterms give sellers minimal responsibility but place all logistics, risk, and costs on buyers. It’s best for buyers who are experienced, have local representatives, or wish to consolidate shipments. Comparing EXW with FOB and other Incoterms helps businesses choose the right shipping agreement. Always consider risk transfer, customs requirements, and insurance to avoid unexpected costs.
By understanding EXW, buyers and sellers can make informed decisions, save costs, and ensure smooth international trade.
References
FAQ
1. What does EXW mean in shipping terms?
EXW (Ex Works) means the seller makes goods available at a specific location, and the buyer is responsible for all transport and related risks from that point onward.
2. Who pays for shipping under EXW?
The buyer pays for all shipping costs, including transport to the port, freight, customs duties, and insurance. The seller only prepares and packages the goods.
3. What is the difference between FOB and EXW?
Under FOB, the seller delivers goods to the port and loads them on the ship, handling export clearance. Under EXW, the seller’s responsibility ends at their premises, and the buyer handles everything after pickup.
4. What are the Incoterms of Ex Works?
EXW is one of the 11 main Incoterms by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining minimal seller responsibility and maximum buyer responsibility. It standardizes delivery, cost, and risk transfer.
5. Who is responsible in EXW?
The buyer is responsible for all transportation, customs, insurance, and delivery costs. The seller only ensures goods are packed, labeled, and ready for pickup.
Tech
Robotics and Automation in 2026: Trends & Impact

Introduction
Robotics and Automation are transforming how industries operate in 2026. From smart factories to advanced healthcare systems, industrial robotics and automation technology are improving speed, safety, and precision. Businesses across the United States are adopting AI integration, machine learning in robotics, and Industry 4.0 solutions to reduce costs and boost productivity. In manufacturing, robots streamline assembly lines. In logistics, automated systems optimize supply chains. Even healthcare now relies on robotic assistance for surgery and patient care. As human-robot collaboration increases, companies must adapt to rapid innovation. Understanding robotics market growth and automation trends helps organizations stay competitive in a fast-changing economy.
Types of Robotics and Automation
Across industries different robotic categories serve unique purposes. In manufacturing heavy duty machines handle welding and packaging and labeling with flawless timing. Meanwhile service robotics assist surgeons and support elderly care in hospitals and homes. Because environments vary widely, each system is engineered for specific outcomes.
Equally important collaborative robots enhance human-robot collaboration in shared spaces. Unlike traditional cages these cobots safely interact with workers. In addition robotic process automation digitizes office workflows and reduces paperwork errors in export documentation and import documentation. Therefore organizations choose systems based on scale, safety, and flexibility needs.
Industrial vs Service Robotics
Industrial machines dominate controlled factory floors. By contrast service robots function in dynamic public settings. For instance automotive plants rely on robotic arms for precision welding. However hospitals use compact robots for delicate surgery. Ultimately both segments contribute to rapid robotics market growth across the United States.
Advantages of Robotics and Automation
Efficiency drives adoption nationwide. Because robots operate without fatigue production continues around the clock. Furthermore automated systems reduce defects and improve risk transfer management in supply chains. Consequently companies experience lower transportation costs and smoother loading and unloading operations at every shipping terminal.
Cost savings also attract executives. Although initial investment feels significant long term returns often outweigh expenses. In addition improved safety protects workers from hazardous environments. For example robots manage extreme heat in metal plants while humans supervise remotely. Thus automation strengthens profitability while preserving well being.
Robotics and Automation in Various Industries
Manufacturing remains the strongest adopter. In automotive facilities robotic systems assemble engines and paint vehicles with microscopic precision. Meanwhile agriculture deploys autonomous tractors that analyze soil data before planting. As a result yields increase while waste declines.
Healthcare presents another powerful case. Robotic surgery enhances accuracy and shortens recovery time. Likewise logistics companies integrate warehouse automation to speed package routing toward the destination port or final delivery location. Even construction firms employ robotic arms to lay bricks faster than traditional crews. Across sectors the momentum continues to build.
| Industry | Primary Automation Use | Core Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Robotic welding | Precision |
| Healthcare | Surgical robots | Safety |
| Agriculture | Smart tractors | Yield growth |
| Logistics | Sorting robots | Faster delivery |
| Construction | Robotic bricklaying | Efficiency |
Impact on Employment and Workforce
Many workers worry about displacement. However the story proves more layered than headlines suggest. While repetitive jobs decline new technical roles expand rapidly. For example demand grows for robotics programmers and maintenance engineers. Therefore education systems emphasize digital literacy and problem solving.
At the same time human-robot collaboration reshapes daily tasks. Instead of replacing workers automation augments capability. Employees supervise systems analyze data and make strategic decisions. Consequently organizations invest heavily in reskilling programs to prepare teams for an automated economy.

Technological Innovations in Robotics
Innovation fuels progress continuously. Thanks to AI integration robots now interpret visual data instantly. Additionally advanced sensors detect pressure temperature and movement with remarkable sensitivity. Because of these improvements machines adapt to unpredictable environments.
Cloud connectivity expands capability further. Through shared databases fleets of robots learn collectively. In parallel edge computing reduces latency and enhances real time responsiveness. As technology evolves automation systems become smarter safer and more autonomous than ever before.
Environmental Sustainability in Robotics and Automation
Sustainability increasingly shapes investment decisions. By optimizing material usage robots significantly reduce waste. Moreover automated recycling systems improve resource recovery in manufacturing plants. Consequently businesses lower emissions while protecting margins.
Renewable energy also benefits. For instance robots maintain wind turbines and solar installations efficiently. In addition digital monitoring minimizes unnecessary travel and energy loss. Therefore automation supports greener production without sacrificing output.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
Governments recognize both opportunity and risk. In the United States safety agencies enforce strict workplace standards for Robotics and Automation deployment. Meanwhile privacy laws address concerns linked to AI driven monitoring systems. Because technology evolves quickly regulations must adapt equally fast.
Liability questions demand clarity as well. If autonomous systems malfunction accountability becomes complex. Therefore policymakers collaborate with industry leaders to build transparent frameworks. Balanced regulation encourages innovation while maintaining public trust.
Global Trends and Market Forecast
Market indicators reveal strong upward momentum. Analysts project global revenue surpassing 280 billion dollars by 2032. North America leads in AI research while Asia Pacific dominates manufacturing scale. Meanwhile Europe invests heavily in sustainability focused robotics.
Looking ahead adoption will broaden beyond large enterprises. As costs decline small businesses will integrate smart automation tools. Ultimately the convergence of automation technology, data analytics, and digital infrastructure positions Robotics and Automation as a cornerstone of future economic growth.
Click her for further guide EXW Incoterms Simplified for Buyers and Sellers (2026)
Conclusion
The rise of Robotics and Automation signals a new industrial era driven by intelligence and efficiency. With continued advances in automation technology, AI integration, and smart manufacturing, businesses can unlock higher productivity and safer workplaces. However, long-term success depends on workforce adaptation, digital skills, and responsible innovation. Companies that embrace human-robot collaboration and invest in scalable automation solutions will lead the future. As the U.S. market accelerates toward full digital transformation, robotics will remain a cornerstone of economic growth and technological progress.
FAQ
What is the role of robotics in the future?
Robotics will enhance productivity, safety, and efficiency across industries. Robots will perform complex tasks alongside humans in manufacturing, healthcare, and daily life.
What is the role of robotics in automation?
Robotics drives automation by executing repetitive or dangerous tasks with precision. They streamline workflows, reduce errors, and lower operational costs.
Why is robotics important in today’s world?
Robotics improves efficiency, consistency, and quality in industrial and service sectors. It also enables innovation in healthcare, logistics, and sustainable solutions.
What are the 4 types of automation?
The four types are fixed automation, programmable automation, flexible automation, and integrated automation. Each serves different production scales and flexibility needs.
What is the future of automation?
Automation will evolve with AI, machine learning, and robotics integration. Smart systems will handle complex tasks, creating safer, faster, and more efficient industries.
Tech
Top Artificial Intelligence Stocks Under $10 to Buy in 2026

Investing in AI stocks under $10 is becoming a smart choice for beginners and budget-conscious investors. Artificial intelligence stocks are growing rapidly as AI technology transforms industries like healthcare, finance, and robotics. Buying cheap AI stocks allows investors to enter the market without spending a fortune while still benefiting from potential growth. In 2026, several affordable artificial intelligence shares show promise for long-term gains. Understanding which low-cost AI stocks to pick can help you make informed investment decisions. This guide highlights the top AI stocks under $10 that combine affordability with strong growth potential in the fast-evolving AI market.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence Stocks
Artificial Intelligence stocks belong to companies that develop, apply, or benefit from AI technology. These companies often focus on machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, automation, or data analytics.
For example, machine learning builds models that analyze data and predict outcomes. Natural language processing allows AI to understand and generate human language, while computer vision interprets visual data, such as facial recognition or self-driving cars.
Additionally, automation and robotics replace manual tasks, and data analytics provides actionable insights for businesses. Because of this, the AI market is expected to exceed $1 trillion globally within a few years. Consequently, even small-cap AI companies are racing to launch new AI-powered tools and platforms.
Why Focus on AI Stocks Under $10?
Stocks under $10 attract attention due to affordability and growth potential. Moreover, buying low-cost stocks allows investors to purchase more shares and potentially gain large returns.
1. Entry-Level Accessibility
Low-priced stocks make it easier for beginners to invest. In addition, you don’t need thousands of dollars to build a diversified AI-focused portfolio.
2. Early-Stage Innovation
Many sub-$10 AI companies are still in early development. Although they may not yet be profitable, they are creating unique AI technologies that could disrupt industries in the future.
3. High Growth Potential
If an AI startup secures a major partnership, government contract, or product success, its stock can increase significantly. Therefore, small investments today may yield large returns tomorrow.
4. Portfolio Diversification
Adding a few small AI stocks under $10 helps spread risk. Furthermore, it gives exposure to a fast-growing sector without requiring a large investment.
Risks of Investing in AI Stocks Under $10
While the potential gains are exciting, it is important to consider the risks of low-cost AI stocks.
1. Volatility
Low-priced stocks fluctuate dramatically. For instance, a 20–30% move in a single day is not uncommon. As a result, investors must be prepared for rapid swings in value.
2. Limited Resources
Smaller AI companies may lack financial stability. Consequently, if products fail or funding dries up, the stock can lose most of its value.
3. Speculation Over Fundamentals
Some companies call themselves AI-driven to attract investors, even when AI integration is minimal. Therefore, always research AI companies thoroughly before investing.
4. Market Manipulation
Penny stocks (under $5) are sometimes prone to pump-and-dump schemes. On the other hand, companies listed on NASDAQ or NYSE are more regulated and transparent.
Promising Artificial Intelligence Stocks Under $10 (2025)
Here are some AI-related companies trading under $10 that are worth researching. These companies operate in AI software, robotics, automation, and data analytics.

1. BigBear.ai (BBAI)
Overview: Provides AI-driven analytics for defense, manufacturing, and logistics.
Why It’s Interesting: Works with U.S. government agencies and has potential growth from defense contracts.
Key Risks: Dependence on government contracts and slow private adoption.
2. Veritone Inc. (VERI)
Overview: Offers an AI platform that processes audio, video, and text.
Why It’s Interesting: AI-powered transcription, content tagging, and recurring partnerships.
Key Risks: High competition and slow profitability growth.
3. Rekor Systems Inc. (REKR)
Overview: Specializes in AI-based vehicle recognition and traffic analytics.
Why It’s Interesting: Provides real-time roadway intelligence and recurring cloud revenue.
Key Risks: Dependence on government contracts.
4. Guardforce AI (GFAI)
Overview: Offers AI-powered security and robotics in the Asia-Pacific region.
Why It’s Interesting: Combines physical and digital security with AI solutions.
Key Risks: Regulatory challenges in foreign markets.
5. FiscalNote Holdings (NOTE)
Overview: Uses AI to analyze government legislation and policies.
Why It’s Interesting: Subscription-based recurring revenue; growing demand for regulatory insights.
Key Risks: Limited market awareness and uncertain profitability.
6. Lantronix Inc. (LTRX)
Overview: Develops IoT solutions integrated with AI at the edge.
Why It’s Interesting: Exposure to AI edge computing trends and major tech partnerships.
Key Risks: Competition from larger IoT companies.
7. Cyngn Inc. (CYN)
Overview: Focuses on autonomous industrial vehicles like driverless forklifts.
Why It’s Interesting: AI-driven navigation and logistics partnerships.
Key Risks: Early-stage business with uncertain revenue.
How to Evaluate AI Stocks Under $10
Before investing, follow this research checklist:
- Business Model: Hardware, software subscriptions, or services?
- Market Opportunity: Are they targeting sectors like automation or predictive analytics?
- Financial Health: Review revenue, cash flow, and debt.
- Partnerships and Clients: Big contracts validate technology.
- Leadership Team: Experienced management increases success.
- Innovation and IP: Patents and unique AI models give a competitive edge.
- Stock Liquidity: Avoid thinly traded stocks.
- Exchange Listing: Prefer NASDAQ or NYSE for transparency.
Tips for Investing in Low-Priced AI Stocks
- Start Small: Treat as a speculative investment.
- Diversify: Spread across multiple AI companies.
- Focus on Long-Term Trends: Be patient with AI growth.
- Avoid Hype: Look for real AI technology and results.
- Set a Stop-Loss: Protect against emotional selling during volatility.
Long-Term Outlook for AI Stocks
Artificial Intelligence is transforming businesses worldwide from factory automation to predictive analytics in medicine. Analysts expect AI investments to grow exponentially by 2030. Consequently, even smaller companies that survive and scale could see valuations soar. The key is identifying those with strong fundamentals, clear AI-focused business models, and sustainable growth strategies.
Related Artical:
Robotics and Automation in 2026
EXW Incoterms Simplified for Buyers and Sellers (2026)
conclusion
Investing in AI stocks under $10 is a smart way to start your journey in the booming artificial intelligence market. These cheap AI stocks offer affordable opportunities for both beginners and experienced investors to gain from the fast-growing AI industry. By carefully choosing affordable artificial intelligence shares, you can balance risk and potential profit. Always research the company’s growth prospects before investing in any low-cost AI stocks. With the right strategy, AI stocks under $10 can become a valuable addition to your investment portfolio and help you benefit from the future of artificial intelligence technology.
FAQ
- Q1:What is the best AI stock under $10?
One of the top AI stocks under $10 currently is C3.ai (AI), known for its enterprise AI solutions. It offers potential growth for investors seeking affordable artificial intelligence shares. - Q2:What is the cheapest AI stock?
The cheapest AI stocks can vary daily, but smaller companies like Veritone (VERI) often trade under $10. These low-cost AI stocks give beginners an entry into the AI market. - Q3:What is the most promising AI stock?
NVIDIA (NVDA) is considered the most promising due to its AI hardware and software dominance. It plays a key role in artificial intelligence technology growth. - Q4:What’s the best $3 AI stock?
Stocks like Remark Holdings (MARK) have traded around $3, offering potential growth in the AI sector. These are affordable artificial intelligence shares for small investors. - Q5:Who owns 49% of OpenAI?
Microsoft owns a significant stake in OpenAI, investing heavily in its AI development. This partnership strengthens OpenAI’s role in AI innovation and commercial applications.
Tech
EV Technology: The Future of Electric Vehicles and Sustainable Mobility

Introduction
Electric Vehicle Technology (EV Tech) is reshaping the future of transportation. With rising concerns over climate change, fuel dependency, and urban pollution, electric vehicles have emerged as a sustainable alternative to traditional combustion-engine cars. In 2025, EV technology is advancing at record speed, powered by innovations in batteries, charging infrastructure, artificial intelligence, and smart mobility solutions.
This blog explores the fundamentals of EV technology, its benefits, challenges, and the trends that are driving the global transition to electric mobility.
What is EV Technology?
EV technology refers to the systems and innovations that power electric vehicles, replacing conventional fuel-driven engines with electric motors and batteries. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs use stored electrical energy for propulsion, making them cleaner, quieter, and often more cost-efficient.
Key Components of EV Tech include:

- Battery Systems – Store and supply power.
- Electric Motors – Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Charging Infrastructure – Networks that recharge EV batteries.
- Software & AI – Optimize energy efficiency and integrate smart driving features.
Evolution of EV Technology
- Early 19th Century – First prototypes of electric vehicles appeared, but limited by battery technology.
- Late 20th Century – Introduction of hybrid vehicles (e.g., Toyota Prius).
- 2000s – Lithium-ion batteries revolutionized EV performance.
- 2010s – Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet popularized modern EVs.
- 2020s – Emergence of solid-state batteries, wireless charging, and AI-driven EVs.
Core Components of EV Technology
1. Battery Systems
The battery is the heart of an EV.
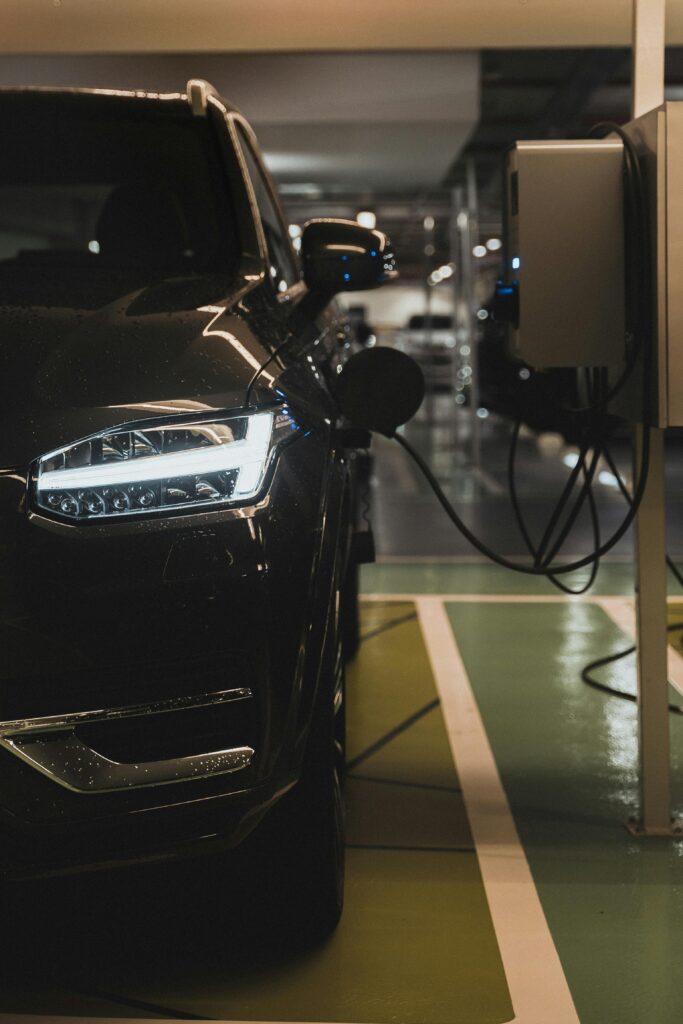

- Lithium-ion Batteries – Current standard, offering balance of cost, weight, and performance.
- Solid-State Batteries – Next-generation tech with faster charging, higher capacity, and safety benefits.
- Battery Recycling – Essential for sustainability, reducing reliance on rare earth metals.
2. Electric Motors
EVs rely on motors instead of engines.
- Induction Motors – Used by Tesla for durability.
- Permanent Magnet Motors – Efficient but depend on rare earth materials.
- Switch Reluctance Motors – Gaining popularity due to efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
3. Charging Infrastructure
- Level 1 (Slow Charging): Household outlets, ~8–12 hours for full charge.
- Level 2 (Fast Charging): Common in homes/offices, 3–6 hours.
- DC Fast Charging: Rapid, ~30 minutes to 1 hour.
- Wireless Charging: Emerging tech for convenience.
4. Software & AI Integration
EVs are as much about software as hardware.
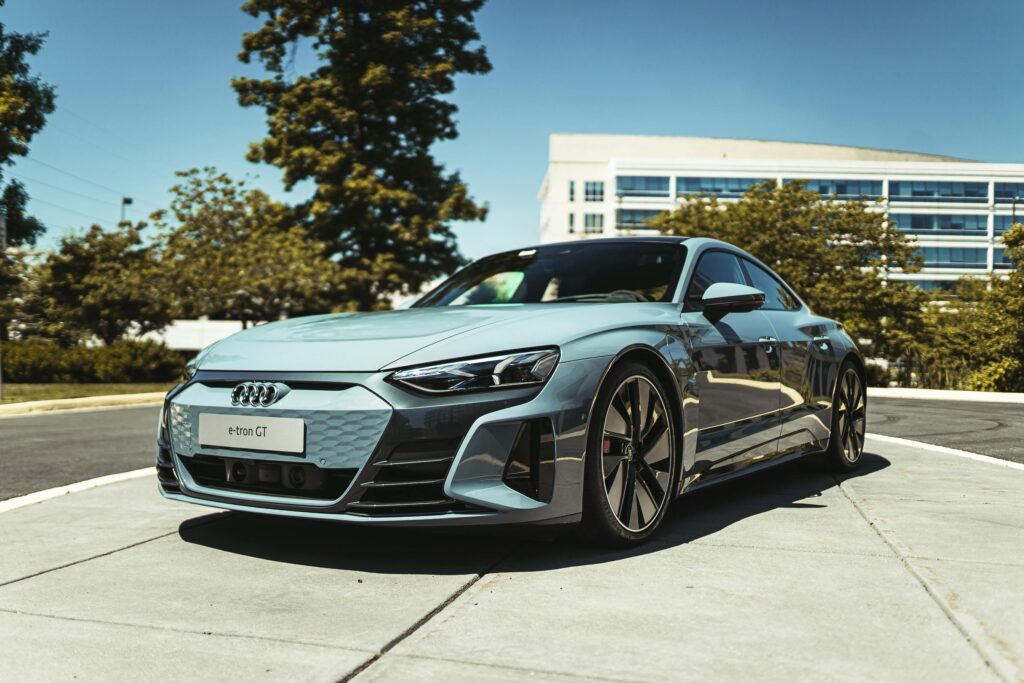

- AI optimizes battery usage.
- Smart navigation suggests charging stations.
- Over-the-air (OTA) updates improve features.
- Integration with autonomous driving systems.
Benefits of EV Technology
- Environmental Sustainability – Zero tailpipe emissions reduce air pollution.
- Lower Operating Costs – Electricity is cheaper than fuel; fewer moving parts mean less maintenance.
- Energy Efficiency – EVs convert ~60% of energy into motion (vs ~20% for ICE vehicles).
- Government Incentives – Tax breaks, subsidies, and priority access to urban areas.
- Noise Reduction – EVs operate quietly, improving urban living conditions.
Challenges Facing EV Technology
- High Initial Cost – Batteries still make EVs more expensive upfront.
- Charging Infrastructure Gaps – Limited access in rural areas.
- Range Anxiety – Fear of running out of charge.
- Battery Life & Recycling Issues – Sustainability concerns remain.
- Grid Demand – Increased EV adoption puts pressure on energy grids.
Future Trends in EV Technology
- Solid-State Batteries – Promising faster charging and greater energy density.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) – EVs feeding power back into grids during peak hours.
- Autonomous EVs – Combining self-driving tech with electric propulsion.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell EVs – Offering long-range clean energy.
- Global Expansion of Charging Networks – Faster and more accessible infrastructure.
Global Adoption of EV Tech
- China – World leader with largest EV market and government support.
- Europe – Strong regulations pushing for 100% EV adoption by 2035.
- United States – Rapid expansion led by Tesla, Rivian, and GM.
- Developing Countries – Gradual adoption due to infrastructure and affordability issues.
EV Tech for Consumers
How to Choose an EV:
- Check battery range.
- Review charging options nearby.
- Compare total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Look for government incentives.
Lifestyle Impact:
- Lower maintenance.
- Eco-conscious driving.
- Need to plan charging stops during long trips.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to charge an EV?
Depends on the charger: Level 1 takes 8–12 hours, while DC fast charging can recharge in under an hour.
2. What is the lifespan of an EV battery?
Typically 8–15 years, depending on usage and technology.
3. Are EVs cheaper to maintain than gas cars?
Yes. Fewer moving parts mean reduced repair costs.
4. Can EVs really reduce carbon emissions?
Yes, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.
5. What’s next for EV technology?
Solid-state batteries, AI-powered driving, and global charging networks.
Conclusion
EV technology is not just a trend it’s the future of transportation. With advancements in batteries, charging infrastructure, and AI integration, EVs are becoming more affordable, efficient, and accessible. Governments and industries worldwide are investing heavily in EV innovation, accelerating the shift toward a greener, smarter, and more sustainable future.
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoWhy ’90s Fashion Still Dominates Today’s Style Scene
-

 How-to Guides6 months ago
How-to Guides6 months agoHow to Restore Pantone Colors in New Illustrator Versions (2026 Guide)
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoTop Fashion Trends to Follow in August 2025
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoReddit Politics in 2026: How Online Political Discourse Shapes Opinions
-

 How-to Guides6 months ago
How-to Guides6 months agoHow to Screenshot on Mac: The Complete 2026 Guide






