Tech & AI Tools
Java Runtime Environment (JRE): Complete SEO-Friendly Guide
Introduction
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is one of the most important components of the Java programming ecosystem. Without JRE, Java applications cannot run on desktops, servers, or mobile devices. It provides everything needed to execute Java programs smoothly and securely. In this blog, you will learn what JRE is, how it works, its components, advantages, disadvantages, and installation methods. This SEO-friendly guide makes it easy for students, beginners, and professionals to understand the Java Runtime Environment.
What is Java Runtime Environment (JRE)?
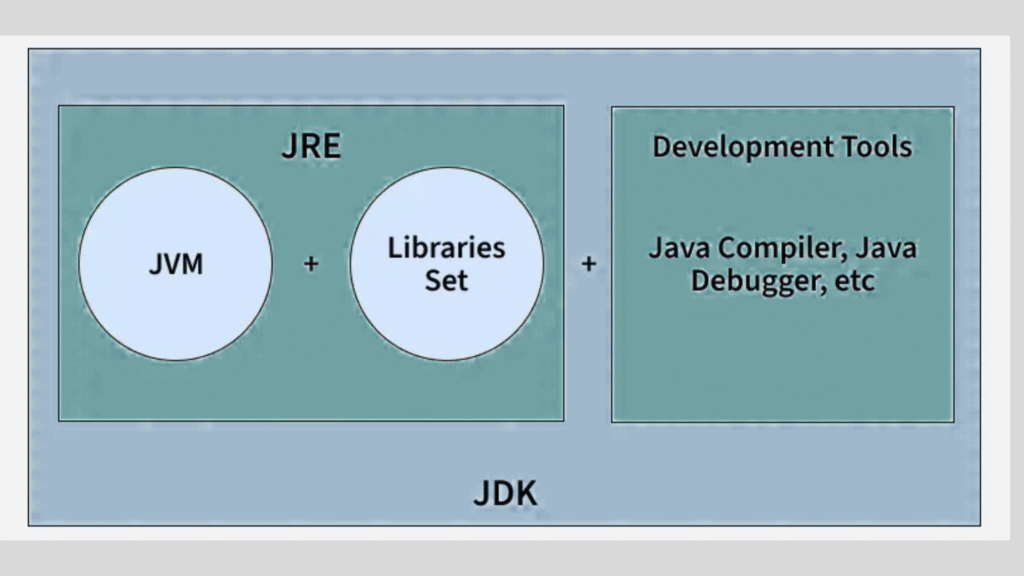
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a software package that creates the environment necessary to run Java applications. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), core Java libraries, and supporting files.
In simple terms:
JRE = JVM + Java Libraries + Supporting Files
It doesn’t include development tools like compilers or debuggers. Those are part of the Java Development Kit (JDK).
Why Do We Need JRE?
JRE is essential because:
- It runs Java programs on your system.
- It provides platform independence (“Write once, run anywhere”).
- It offers built-in security and memory management.
- Popular applications like Minecraft, Eclipse IDE, and banking systems need JRE to function.
Key Components of JRE
1. Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Executes Java bytecode and converts it into machine code.
- Handles memory allocation, garbage collection, and runtime security.
- Makes Java applications platform-independent.
2. Java Class Libraries
These are prebuilt Java packages like:
java.lang– basic language classesjava.util– utilities and data structuresjava.io– input/output operationsjava.net– networking support
These libraries save time by providing reusable code.
3. Supporting Files and Configuration
- Property files
- Security policy files
- Deployment technologies (Java Web Start, plug-ins)
How Does JRE Work?
Here’s a simple step-by-step explanation:
- You write a Java program (Example:
HelloWorld.java). - The Java compiler (
javac) converts it into bytecode (.class file). - When you run the program, JRE takes over.
- JVM inside JRE:
- Loads the class file.
- Verifies bytecode for security.
- Uses Interpreter or JIT (Just-In-Time Compiler) to execute code.
- Output is displayed on your device.
Difference Between JRE, JDK, and JVM
| Feature | JVM | JRE | JDK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Java Virtual Machine | Java Runtime Environment | Java Development Kit |
| Purpose | Executes Java bytecode | Runs Java applications | Develops and runs Java apps |
| Includes | Execution engine only | JVM + Libraries | JRE + Compiler + Tools |
| Needed For | Running Java code | Running Java apps | Creating and running Java apps |
Advantages of JRE
- Cross-platform support
- Automatic memory management
- Secure execution with sandboxing
- Rich collection of class libraries
- Free and open-source versions available (OpenJDK)
Disadvantages of JRE
- Slower than native languages like C++
- Requires regular updates
- Higher memory usage
- Oracle JRE is no longer freely distributed after Java 11
How to Download and Install JRE
Windows Installation
- Visit the official Oracle or OpenJDK website.
- Download the JRE
.exeinstaller. - Run it and follow the installation steps.
- Check installation using Command Prompt:
java -version
Linux Installation
sudo apt update
sudo apt install default-jre
java -version
macOS Installation
- Download JRE
.dmgfile from Oracle. - Install and allow system permissions.
- Verify using Terminal:
java -version
Popular JRE Versions
| Version | Status | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| JRE 8 | Most widely used | Enterprise applications |
| JRE 11 | Long-Term Support (LTS) | Modern web apps |
| JRE 17 | Latest LTS | Future-proof projects |
| OpenJRE | Open-source | Free use and development |
Applications That Use JRE
- Minecraft Java Edition
- Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, NetBeans
- Banking and ATM software
- Apache Tomcat and GlassFish servers
- Data science and research tools
Tips to Optimize JRE Performance
- Keep Java updated.
- Allocate sufficient memory using
-Xmsand-XmxJVM options. - Use the latest Garbage Collection (GC) algorithms like G1GC.
- Remove unused or outdated Java versions.
- Enable Java security settings to prevent malware.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I run Java programs without JRE?
No. JRE is necessary to run Java applications.
2. What is the difference between JRE and JDK?
JRE runs Java programs, while JDK is used to develop and run them.
3. Is JRE free?
OpenJDK-based JRE is free. Oracle JRE is restricted after Java 11.
4. What command checks Java version?
Use:
java -version
Conclusion
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is the foundation for running all Java applications. It includes essential tools like JVM and Java libraries that make software reliable, secure, and platform-independent. Whether you’re a beginner, student, developer, or gamer, understanding JRE helps you use Java more effectively.
Java continues to power millions of devices worldwide and JRE makes that possible.