Politics
Big Stick Diplomacy: History, Impact, and Modern Lessons

Introduction
Foreign policy has always been shaped by power, diplomacy, and national interest. Throughout history, different leaders have introduced unique approaches to dealing with other nations, ranging from peaceful negotiations to outright wars. One of the most notable approaches in American history was Big Stick Diplomacy, a strategy popularized by President Theodore Roosevelt in the early 20th century.
The phrase comes from Roosevelt’s famous proverb:
“Speak softly and carry a big stick; you will go far.”
At its core, this philosophy combined peaceful diplomacy with the implicit threat of military power. It meant negotiating calmly and respectfully but always being ready to enforce America’s interests with strength if needed.
In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the origins of Big Stick Diplomacy, its historical context, its successes and criticisms, and its relevance in today’s world.
The Origins of Big Stick Diplomacy
Big Stick Diplomacy emerged during Roosevelt’s presidency (1901–1909), at a time when the United States was rapidly growing in power. Several factors shaped this foreign policy approach:
- Spanish-American War (1898): The U.S. victory gave America new territories, such as Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. This marked the country’s entry as a global power.
- Industrial Growth: The U.S. economy was booming, fueling the need for overseas markets and trade routes.
- Military Expansion: Roosevelt believed that a strong navy was essential for global influence. He famously supported building the “Great White Fleet,” a powerful naval force.
- Roosevelt’s Personality: Known for his assertive and bold leadership, Roosevelt naturally favored a proactive and sometimes aggressive approach in international relations.
Core Principles of Big Stick Diplomacy
Big Stick Diplomacy wasn’t just about military threats. It was a comprehensive philosophy with several guiding principles:
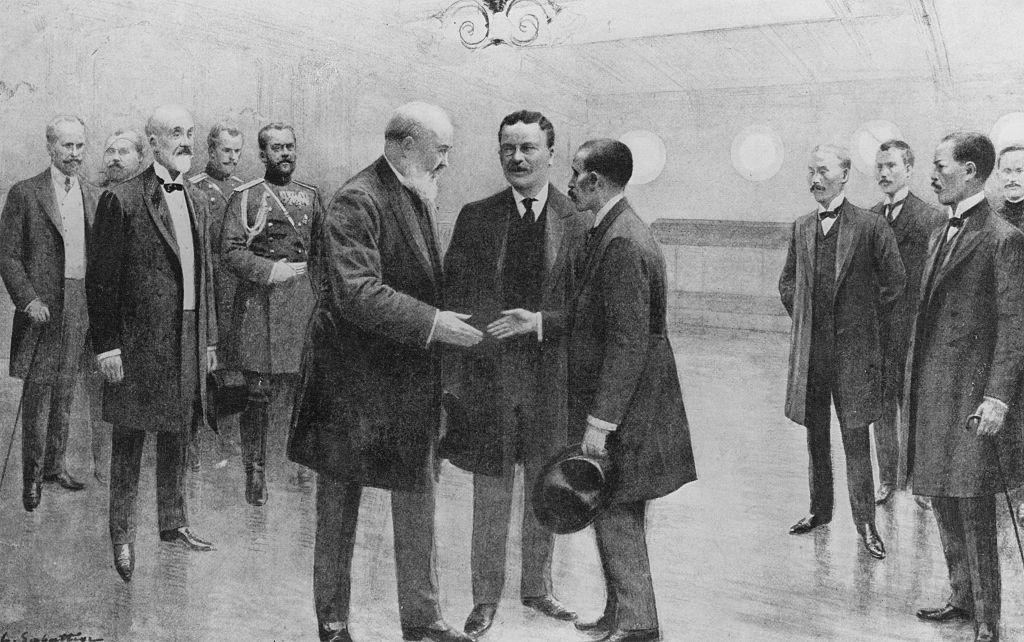

- Peaceful Negotiation First: Diplomacy was always the first option. Roosevelt didn’t believe in unnecessary wars.
- Military Readiness: A strong, modern navy was kept on standby to protect U.S. interests.
- American Leadership: The U.S. saw itself as the guardian of order in the Western Hemisphere.
- Moral Responsibility: Roosevelt often justified interventions as efforts to bring stability and prevent European interference.
Key Applications of Big Stick Diplomacy
1. The Panama Canal
One of the biggest achievements of Big Stick Diplomacy was the construction of the Panama Canal, which connected the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Roosevelt supported Panama’s independence from Colombia to secure U.S. control of the canal zone.
- While controversial, this move gave America a vital strategic and economic advantage.
- The canal became a symbol of American power and engineering capability.
2. The Roosevelt Corollary (1904)
This was an extension of the Monroe Doctrine. Roosevelt declared that the U.S. had the right to intervene in Latin American countries if they were unstable or unable to pay debts to European powers.
- It positioned the U.S. as the “policeman” of the Western Hemisphere.
- It justified multiple interventions in countries like the Dominican Republic, Cuba, and Nicaragua.
3. The Great White Fleet (1907–1909)
Roosevelt sent 16 battleships on a world tour to showcase American naval power.
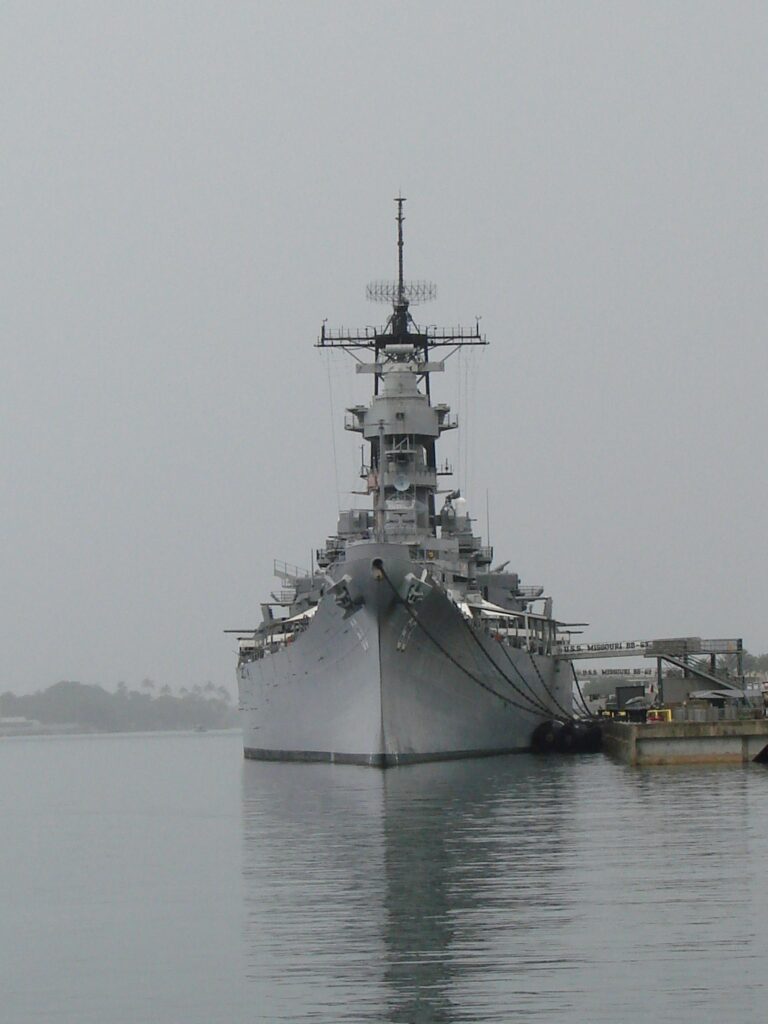

- This wasn’t an act of war, but a show of strength.
- It demonstrated America’s readiness to enforce its interests globally.
4. Russo-Japanese War Mediation (1905)
Interestingly, Big Stick Diplomacy also worked in peaceful ways. Roosevelt mediated peace between Russia and Japan, earning him the Nobel Peace Prize.
- This showcased that “speaking softly” could bring results when backed by power.
Advantages of Big Stick Diplomacy
Big Stick Diplomacy had several notable benefits for the U.S.:
- Strengthened Global Position: It established America as a global power, especially in Latin America and Asia.
- Secured Economic Interests: The Panama Canal and access to new markets boosted trade and industry.
- Deterrence Effect: The mere presence of U.S. naval power often prevented conflicts without direct fighting.
- Peace Through Strength: Roosevelt’s philosophy showed that readiness for war could actually prevent wars.
Criticisms of Big Stick Diplomacy
Despite its successes, the policy was not without its flaws and controversies:
- Imperialism Accusations: Critics argued that it was simply a form of American imperialism, expanding control over weaker nations.
- Resentment in Latin America: U.S. interventions created long-lasting resentment and distrust in Latin America.
- Undermining Sovereignty: By acting as a “policeman,” the U.S. often disregarded the independence of smaller nations.
- Overreliance on Military Power: Some historians believe that this approach normalized the use of force in diplomacy.
Big Stick Diplomacy vs. Other U.S. Foreign Policies
To fully understand Roosevelt’s approach, it’s useful to compare it with other American foreign policies:
- Dollar Diplomacy (President Taft): Focused on using economic investments to influence nations rather than military power.
- Moral Diplomacy (President Wilson): Emphasized spreading democracy and human rights instead of imperialism.
- Isolationism: Earlier presidents preferred to avoid entangling alliances, but Roosevelt embraced active global leadership.
Long-Term Impact
The legacy of Big Stick Diplomacy is still felt today:

- Foundation for Modern U.S. Foreign Policy: The idea of maintaining strong military readiness while pursuing diplomacy continues.
- U.S. Role in Latin America: Interventions created patterns of dependency and mistrust that influence relations even now.
- Military as a Diplomatic Tool: Modern presidents often rely on military strength as leverage in negotiations, echoing Roosevelt’s strategy.
Big Stick Diplomacy in Today’s World
Although Roosevelt’s era is long gone, the philosophy of Big Stick Diplomacy still influences global politics.
- United States: Modern U.S. foreign policy still relies on military strength as a backdrop for diplomacy. For example, negotiations with North Korea or Iran often include the unspoken threat of military action.
- China: As China grows militarily, it is applying a similar strategy in the South China Sea—using its navy to back up diplomatic claims.
- Russia: Russia’s actions in Ukraine and other regions reflect a “speak softly, but show military power” strategy, although often more aggressive.
This shows that the balance between diplomacy and force is still central in world politics.
Lessons for the Future
Big Stick Diplomacy offers both positive and negative lessons for today’s leaders:
- Positive:
- Always back diplomacy with strength.
- Military power can prevent wars if used wisely.
- Leadership requires both negotiation skills and deterrence power.
- Negative:
- Overusing force breeds resentment.
- Nations must respect sovereignty and avoid unnecessary intervention.
- True global leadership comes from cooperation, not domination.
Conclusion
Big Stick Diplomacy remains one of the most fascinating strategies in American history. Rooted in Theodore Roosevelt’s bold personality, it symbolized a mix of negotiation, strength, and readiness to act. While it helped the United States rise as a global power, it also sparked criticism for its imperialistic tendencies.
The proverb “speak softly and carry a big stick” still resonates in today’s world. Nations continue to walk the fine line between diplomacy and military power. The biggest lesson from Roosevelt’s approach is that strength must serve peace, not domination.
FAQs on Big Stick Diplomacy
Q1: Who created Big Stick Diplomacy?
Theodore Roosevelt, the 26th President of the United States, introduced Big Stick Diplomacy during his presidency (1901–1909).
Q2: What does “speak softly and carry a big stick” mean?
It means negotiate peacefully and respectfully, but always be prepared to use strength if necessary.
Q3: What was the main goal of Big Stick Diplomacy?
Its main goal was to protect U.S. interests abroad, especially in Latin America, while preventing European interference.
Q4: What is the Roosevelt Corollary?
An extension of the Monroe Doctrine, it justified U.S. intervention in Latin American countries to maintain stability.
Q5: Why was Big Stick Diplomacy criticized?
Critics saw it as imperialism, arguing it undermined the sovereignty of smaller nations and fostered resentment.
Q6: Is Big Stick Diplomacy still relevant today?
Yes, many nations—including the U.S.—still follow the principle of combining diplomacy with the backing of military strength.
Politics
Understanding Grassroots Movements: Power, Purpose, and Examples That Changed the World

Introduction
In every era, real change often begins not in the halls of power but in the hearts of ordinary people. Grassroots movements embody this idea they start small, grow organically, and influence society from the bottom up.
From the civil rights marches in the 1960s to modern climate activism and digital social justice campaigns, grassroots movements have shaped political, social, and environmental landscapes worldwide. These movements demonstrate how collective community action can challenge institutions, alter public opinion, and reshape laws.
In this article, we’ll explore what a grassroots movement is, how it works, why it’s effective, and the major examples that have changed the world.
What Is a Grassroots Movement?
A grassroots movement is a social or political campaign initiated by ordinary citizens to bring about change at local, national, or global levels.
The term “grassroots” symbolizes something that grows naturally from the ground meaning the movement originates with the people, not with governments or corporations.
Unlike top-down initiatives (where leaders or organizations impose decisions), grassroots movements are bottom-up efforts. They rely on community participation, volunteer action, and collective leadership.
Key Characteristics of Grassroots Movements:
- People-driven: Formed by citizens, not elites or political leaders.
- Local beginnings: Often start within small communities or groups.
- Collective action: Success depends on unity, collaboration, and participation.
- Focus on social change: Aim to address injustice, inequality, or public concerns.
- Low-cost mobilization: Use community resources, social networks, and volunteers.
- Adaptability: Able to evolve with time, technology, and challenges.
How Grassroots Movements Begin
Most grassroots movements start when a group of people notice an unresolved problem that affects them directly whether it’s related to environmental pollution, human rights, education, healthcare, or governance.
Stages of Growth:
- Awareness:
People recognize an issue and begin discussing it within communities, schools, or social media. - Organization:
Activists form local groups, committees, or online networks to share ideas and coordinate action. - Mobilization:
The group organizes protests, petitions, and awareness campaigns to attract attention and supporters. - Advocacy:
Leaders emerge, crafting messages and policies to influence decision-makers or legislation. - Sustainability:
The movement adapts to new challenges, builds partnerships, and maintains momentum for long-term change.
Why Grassroots Movements Are Powerful

- Authentic Representation:
Grassroots movements represent real community voices, making them harder to ignore. - Collective Empowerment:
They give people a sense of purpose and agency, turning frustration into action. - Moral Authority:
Since they often arise from lived experiences, these movements carry moral weight. - Cost-Effective Mobilization:
Social media and digital tools make it easier to spread messages with minimal funding. - Pressure on Institutions:
Persistent community activism can influence policies, elections, and corporate behavior. - Social Cohesion:
By bringing diverse individuals together under one cause, grassroots movements strengthen social unity.
Historical Examples of Grassroots Movements
Let’s look at some of the most influential grassroots movements that have changed history.
1. The Civil Rights Movement (1950s–1960s, USA)
One of the most iconic grassroots efforts, the Civil Rights Movement was led by ordinary African Americans demanding equal rights and an end to racial segregation.
Figures like Rosa Parks, Martin Luther King Jr., and thousands of unsung activists organized boycotts, marches, and peaceful protests.
Impact:
- Passage of the Civil Rights Act (1964) and Voting Rights Act (1965).
- Transformation of racial justice and human rights globally.
2. India’s Independence Movement (1880s–1947)
Before India gained independence from British rule, local citizens organized numerous grassroots campaigns emphasizing nonviolent resistance and self-reliance.
Under Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy of Satyagraha (truth and nonviolence), millions joined boycotts, salt marches, and strikes.
Impact:
- Empowered a colonized population to achieve self-governance.
- Inspired global movements for decolonization and civil rights.
3. The Anti-Apartheid Movement (1948–1994, South Africa)
This movement began at the grassroots level among oppressed Black South Africans who resisted the apartheid system of racial segregation.
Nelson Mandela, Desmond Tutu, and countless activists mobilized local and international support to fight injustice.
Impact:
- Led to the dismantling of apartheid laws.
- Established a democratic South Africa in 1994.
4. The Arab Spring (2010–2012)
The Arab Spring began with local protests in Tunisia and spread across the Middle East. Citizens used social media platforms to organize demonstrations against corruption and authoritarian rule.
Impact:
- Toppled regimes in several countries (e.g., Tunisia, Egypt).
- Demonstrated the power of digital grassroots activism.
5. Fridays for Future (2018–Present)
Started by Swedish teen Greta Thunberg, this climate movement began as a solo protest and grew into a global youth-led campaign for environmental justice.
Impact:
- Millions of students participated in climate strikes.
- Pushed governments to adopt stronger environmental policies.
Modern Digital Grassroots Movements
In the digital age, grassroots movements no longer rely solely on physical gatherings. They thrive through social media, online petitions, and crowdfunding platforms.
Examples:
- #MeToo Movement: Empowered survivors of sexual harassment to speak out globally.
- Black Lives Matter (BLM): Originated from social media hashtags and became a worldwide campaign for racial justice.
- Extinction Rebellion: Uses peaceful civil disobedience to demand government action on climate change.
- Occupy Wall Street: Sparked a global conversation on economic inequality and corporate power.
Tools That Empower Grassroots Movements
- Social Media Platforms:
Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok enable rapid information sharing and mobilization. - Crowdfunding Sites:
Platforms like GoFundMe and Patreon allow activists to fund campaigns without institutional support. - Messaging Apps:
WhatsApp and Telegram groups help organizers coordinate privately and securely. - Online Petitions:
Websites like Change.org make it easier for people to advocate for change and gather signatures. - Community Radio and Podcasts:
Offer accessible platforms for spreading awareness in local languages and cultures.
Challenges Faced by Grassroots Movements
Despite their influence, grassroots movements face multiple obstacles:

- Funding Limitations:
Many rely on volunteers and donations, which may limit long-term sustainability. - Internal Conflicts:
Disagreements about leadership, strategy, or messaging can weaken unity. - Government Suppression:
Authorities may criminalize protests, censor social media, or intimidate activists. - Misinformation:
False information or propaganda can distort public perception. - Short Public Attention Span:
In the digital era, viral moments fade quickly without strategic follow-up. - Burnout:
Continuous activism can emotionally exhaust participants, especially volunteers.
Keys to a Successful Grassroots Movement
To succeed, grassroots organizers must blend authentic passion with strategic planning. Here are essential ingredients for lasting impact:
- Clear Vision:
Define specific goals and communicate them effectively. - Strong Leadership:
Empower local leaders who can motivate and organize others. - Community Involvement:
Build trust and ensure local participation in every decision. - Inclusive Messaging:
Avoid division unify diverse communities under one purpose. - Partnerships:
Collaborate with NGOs, media, and institutions for greater reach. - Persistence:
Change takes time; consistent action and patience are crucial.
Grassroots vs. Top-Down Movements
| Aspect | Grassroots Movement | Top-Down Movement |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Starts from citizens and communities | Initiated by leaders or institutions |
| Structure | Horizontal, participatory | Hierarchical |
| Funding | Local donations and volunteers | Government or corporate support |
| Decision-making | Collective and democratic | Centralized |
| Example | Civil Rights Movement | Government-sponsored reform campaigns |
Impact of Grassroots Movements on Society
Grassroots movements have a long-lasting impact that goes beyond immediate results. They change how people think, engage, and demand accountability.
Social Impact:
- Promote equality, justice, and human rights.
- Encourage civic education and participation.
Political Impact:
- Influence legislation and policy changes.
- Hold leaders accountable for promises and corruption.
Cultural Impact:
- Shift social norms (e.g., gender equality, environmental awareness).
- Inspire art, literature, and community media.
The Future of Grassroots Movements
The future of grassroots activism lies in hybrid organizing blending on-ground action with digital advocacy.
Technologies like AI, blockchain, and crowdsourced data can strengthen transparency and mobilization. However, activists must stay vigilant against digital surveillance and misinformation.
Global youth, empowered by education and technology, will continue driving grassroots movements on climate change, gender rights, and social justice ensuring that people’s voices remain powerful forces for transformation.
Conclusion
A grassroots movement proves that true power lies within the people. Whether sparked by injustice, inequality, or environmental crises, these movements remind us that change begins from the bottom with individuals who refuse to remain silent.
From Gandhi’s independence struggle to Greta Thunberg’s climate crusade, grassroots movements continue to redefine what collective action can achieve. In a world where voices are easily drowned out by power and profit, grassroots activism remains a timeless reminder: real change grows from the ground up.
Business
Trade Agreements: Building Bridges in Global Commerce

Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, no nation can remain isolated when it comes to trade. Countries depend on each other for resources, technology, and markets. This interdependence has given rise to trade agreements, formal arrangements between nations that establish rules and guidelines for exchanging goods, services, and investments. Trade agreements are critical for boosting economic growth, reducing trade barriers, and fostering cooperation across borders.
This blog explores the types of trade agreements, their benefits, challenges, and examples, while also answering frequently asked questions.
What Are Trade Agreements?
It is a contract or treaty between two or more nations that outlines the terms of trade between them. These agreements are designed to:

- Reduce or eliminate tariffs, quotas, and duties.
- Simplify customs procedures.
- Promote fair competition.
- Protect intellectual property rights.
- Encourage investments.
Trade agreements are binding under international law and can be bilateral (between two countries) or multilateral (involving multiple countries).
Importance
- Economic Growth : By opening markets, agreements increase exports and imports, creating opportunities for businesses.
- Job Creation : Expanding trade often leads to new industries and jobs in both manufacturing and services.
- Access to Resources : Nations can access raw materials, technology, and goods that may not be available domestically.
- Global Competitiveness : Trade agreements push businesses to innovate and improve efficiency.
- Political Cooperation : Strong economic ties often reduce conflicts and build diplomatic trust.
Types
1. Bilateral Trade Agreements
- Agreements between two nations.
- Example: The U.S.–Mexico Agreement on sugar exports.
2. Multilateral Trade Agreements
- Agreements involving multiple countries.

- Example: The World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements that regulate trade globally.
3. Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs)
- Nations within a specific geographic area form agreements.
- Example: European Union (EU), North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (now replaced by USMCA).
4. Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Eliminate tariffs and quotas among member nations.
- Example: ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) in Southeast Asia.
5. Customs Unions
- Member nations adopt a common external tariff system.
- Example: The Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR) in South America.
6. Common Market Agreements
- Allow free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor.
- Example: European Single Market.
Key Examples
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) → USMCA
- Established in 1994 between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
- In 2020, replaced by United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA).
- Focused on reducing tariffs, protecting intellectual property, and promoting fair labor practices.
European Union (EU) Single Market
- One of the most advanced trade blocs in the world.
- Allows goods, services, capital, and people to move freely across member states.
World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreements
- WTO was established in 1995.
- Provides a platform for negotiating and enforcing global trade rules.
Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
- Involves countries like Japan, Canada, Australia, and Mexico.
- Promotes free trade in the Asia-Pacific region.
African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
- Aims to create a single market across Africa.
- Could boost intra-African trade significantly.
Benefits of Trade Agreements
- Lower Costs for Consumers : Reduced tariffs make imported goods cheaper.
- Expanded Business Opportunities : Companies gain access to international markets.
- Encouragement of Innovation : Competition drives businesses to adopt new technologies.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) : Trade agreements attract investors seeking access to larger markets.
- Stronger Diplomatic Ties : Economic interdependence strengthens relationships between nations.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Unequal Benefits : Not all industries or countries benefit equally.
- Job Losses : Certain domestic industries may suffer due to increased imports.
- Dependence on Imports : Over-reliance on foreign goods can weaken local industries.
- Environmental Concerns : Increased production and shipping can harm ecosystems.
- Complex Negotiations : Reaching consensus among multiple countries can take years.
Future of Trade Agreements
With globalization, trade agreements are evolving. Emerging trends include:
- Digital Trade Agreements : Covering e-commerce, cybersecurity, and data protection.
- Green Trade Policies : Incorporating climate change and sustainability measures.
- Regional Blocs Expansion : More countries joining existing agreements.
- Focus on Fair Trade : Ensuring labor rights, wage standards, and ethical sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between free trade and fair trade?
- Free trade focuses on reducing tariffs and quotas.
- Fair trade emphasizes ethical practices, fair wages, and sustainability in trade.
2. Do trade agreements benefit all countries equally?
No. Larger economies often benefit more due to stronger industries, while smaller economies may struggle to compete. However, they can gain from access to bigger markets.
3. Why do some people oppose trade agreements?
Opposition comes from concerns about job losses, outsourcing, environmental damage, and loss of local industry competitiveness.
4. How do trade agreements affect consumers?
Consumers benefit from lower prices, more choices, and better quality products. However, domestic producers may face tougher competition.
5. Can trade agreements fail?
Yes. If countries don’t comply with rules or economic conditions change drastically, agreements may collapse or need renegotiation. Example: NAFTA was renegotiated into USMCA.
6. What role does the WTO play in trade agreements?
The WTO acts as a global referee, ensuring nations follow trade rules, settling disputes, and promoting fair competition.
7. How do trade agreements support developing countries?
They provide access to larger markets, encourage investments, and help nations integrate into the global economy.
Conclusion
Trade agreements are the backbone of global commerce. While they come with challenges, their role in shaping economies, creating opportunities, and fostering international cooperation cannot be underestimated. The future of trade will likely be defined by digitalization, sustainability, and inclusivity. For businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike, understanding trade agreements is essential in today’s globalized economy.
Politics
Reddit Politics: A Deep Dive into Online Political Discourse

Introduction
In today’s digital era, online communities play a huge role in shaping political opinions, driving debates, and even influencing elections. Among the many platforms where politics is discussed, Reddit Politics stands out as one of the most active, controversial, and impactful. With millions of users worldwide, Reddit’s politics-related communities most notably the r/politics subreddit have become a hub for breaking news, opinion sharing, activism, and heated discussions.
But what exactly is Reddit Politics? How does it shape the political landscape? Why has it become both a trusted and controversial space for news and debates? This blog will explore everything you need to know about Reddit Politics, from its history and community rules to its role in modern democracy and media consumption.
What is Reddit Politics?
Reddit Politics generally refers to the political communities on Reddit, the most prominent being r/politics, a subreddit with over 10 million members. Reddit itself is a massive forum-based social media site where users share links, ask questions, and engage in discussions. Unlike traditional news outlets, Reddit thrives on user-generated content and upvotes, which decide what becomes visible.
Key Features of r/politics
- User-driven content: Anyone can post political news, opinion pieces, or discussions.
- Upvotes and downvotes: Posts and comments rise or fall in visibility depending on user votes.
- Strict moderation: r/politics has clear rules, often criticized for bias, that control what content is allowed.
- Community debates: The comment sections often host intense debates between users of different political ideologies.
The Rise of Reddit Politics
The subreddit r/politics was created in 2007, and since then, it has become one of the most visited places on Reddit. The platform gained major attention during the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election, when Reddit users actively discussed candidates like Donald Trump, Hillary Clinton, and Bernie Sanders.
Some major milestones in Reddit Politics’ rise include:
- 2012 Presidential Elections: Reddit hosted an “Ask Me Anything” (AMA) session with Barack Obama, bringing huge credibility to the platform.
- 2016 Election Cycle: Political memes, leaks, and grassroots movements thrived on Reddit.
- 2020 U.S. Elections: Reddit became a battleground for discussions around Trump, Biden, COVID-19 policies, and Black Lives Matter.
Influence on Public Opinion
One of the biggest questions about Reddit Politics is whether it truly influences public opinion or merely reflects it. While Reddit is not as mainstream as Facebook or Twitter, its political communities have a reputation for being ahead of the news cycle.

How Reddit Politics Shapes Opinions
- Breaking News First : Many stories surface on Reddit before mainstream outlets cover them.
- Amplifying Grassroots Movements : Reddit has been used to organize protests, petitions, and fundraising campaigns.
- Fact-Checking and Crowd Wisdom : Users often dissect news articles, expose misinformation, and provide sources.
- Echo Chambers and Polarization : Like other social media platforms, Reddit Politics can become an echo chamber where like-minded individuals reinforce each other’s beliefs.
Criticism and Controversies
Despite its influence, Reddit Politics has not escaped controversy.
Common Criticisms
- Moderation Bias: Critics argue that r/politics leans heavily toward liberal or progressive views, with conservative opinions often downvoted or removed.
- Echo Chamber Effect: The subreddit is accused of being one-sided, reducing healthy debate.
- Misinformation: Despite efforts to fact-check, fake news and misleading headlines sometimes gain traction.
- Toxicity in Discussions: Heated political debates can quickly escalate into personal attacks.
Famous Controversies
- 2016 DNC Leak Discussions: The subreddit faced backlash for allegedly censoring WikiLeaks-related posts.
- COVID-19 Misinformation: Political arguments over masks, vaccines, and government policies flooded the subreddit.
- Censorship Allegations: Critics from across the political spectrum accuse moderators of silencing dissent.
Comparing Reddit Politics to Other Platforms
Reddit Politics is unique compared to Twitter, Facebook, and TikTok.
- Twitter/X: More direct engagement with politicians, but limited character count.
- Facebook: Older demographic, with algorithm-driven feeds that can push extreme content.
- TikTok: Short-form video debates, often less fact-based and more emotional.
- Reddit Politics: Long-form discussions, crowd-sourced content, and a more “community-driven” feel.
This makes Reddit Politics a middle ground between mainstream media and grassroots discussions.

Role in Elections
Reddit Politics has played a significant role in elections, especially in the U.S.
- Obama’s 2012 AMA gave Reddit political legitimacy.
- Sanders’ 2016 campaign benefited from huge grassroots support on Reddit.
- 2020 elections saw users mobilize around issues like mail-in ballots, racial justice, and pandemic policies.
Researchers suggest Reddit users are younger, more politically active online, and more likely to influence real-world conversations.
Global Reach of Reddit Politics
Although Reddit Politics is heavily U.S.-centric, international politics also appear in discussions. Events like Brexit, the war in Ukraine, and climate change policies get massive attention. Subreddits like r/ukpolitics, r/worldpolitics, and r/geopolitics extend the reach beyond America.
Benefits of Reddit Politics
- Provides a diverse pool of information and perspectives.
- Encourages political literacy among younger users.
- Offers a space for grassroots activism.
- Facilitates direct communication between public figures and ordinary citizens.
The Future of Reddit Politics
As politics continues to intertwine with digital spaces, Reddit Politics is expected to remain influential. Some possible future trends include:
- Increased Role in Elections : More candidates may use Reddit to connect with voters.
- AI and Moderation : AI tools may help reduce misinformation and bias in moderation.
- Global Expansion : Non-U.S. political subreddits could rise in popularity.
- Greater Scrutiny : As Reddit grows, lawmakers may scrutinize its political impact more closely.
Conclusion
Reddit Politics is more than just a subreddit bit’s a reflection of how politics has transformed in the internet age. It gives ordinary people a voice, challenges mainstream media narratives, and influences how young voters think about politics. At the same time, it faces challenges of moderation, bias, and misinformation.
As the world becomes increasingly digital, platforms like Reddit Politics will continue to shape political conversations in ways we are only beginning to understand. Whether you see it as a force for democracy or a flawed echo chamber, one thing is clear: Reddit Politics is here to stay.
FAQs
1. What is Reddit Politics?
Reddit Politics refers to political discussions on Reddit, primarily in the r/politics subreddit.
2. Is r/politics biased?
Critics say it leans liberal, though moderators claim to enforce neutrality.
3. Can Reddit influence elections?
Yes, Reddit has amplified movements and helped campaigns connect with younger voters.
4. Is Reddit a reliable source for political news?
It can be useful, but users should always cross-check sources.
5. What makes Reddit Politics unique?
Its community-driven format, long discussions, and upvote system set it apart from other platforms.
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoWhy ’90s Fashion Still Dominates Today’s Style Scene
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoTop Fashion Trends to Follow in August 2025
-

 How-to Guides6 months ago
How-to Guides6 months agoHow to Restore Pantone Colors in New Illustrator Versions (2026 Guide)
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoReddit Politics: A Deep Dive into Online Political Discourse
-

 How-To Tutorials & Troubleshooting6 months ago
How-To Tutorials & Troubleshooting6 months agoHow to Screenshot on Mac: The Complete 2025 Guide






