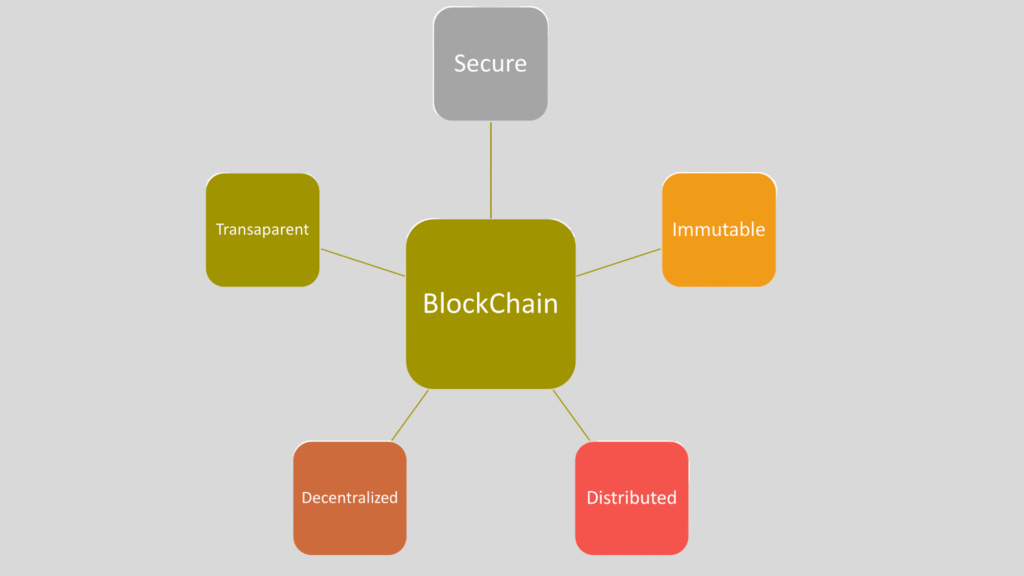
Business
How Does a Hash Help Secure Blockchain Technology?

Introduction
When people hear the term blockchain, they often think of Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, or digital transactions and How Does a Hash Help Secure Blockchain . But behind the scenes, the real hero of blockchain security is something much smaller and technical: the hash function.
A hash is a cryptographic tool that ensures data integrity, security, and immutability in blockchain technology. Without hashing, blockchain would not be able to provide its famous features like decentralization, tamper-proof records, and transparent trust.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- What a hash is and how it works
- Different types of hashing algorithms
- The role of hashing in blockchain
- How hashing ensures security, immutability, and trust
- Real-world applications of blockchain hashing
- Challenges and future of hashing in blockchain
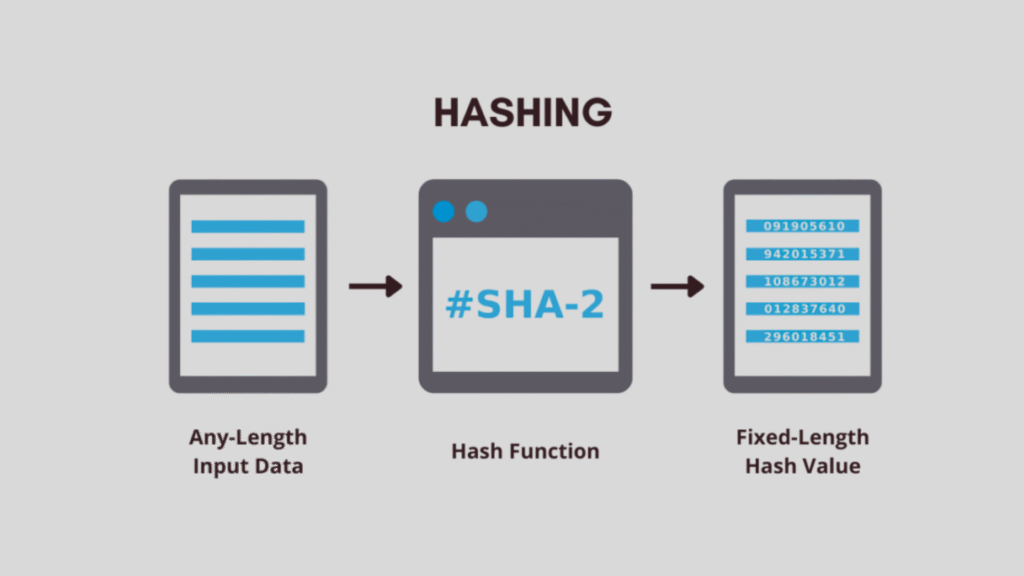
What is a Hash?
A hash is the output of a cryptographic function that takes an input (data of any size) and produces a fixed-length string of characters.
For example:
- Input: “Blockchain”
- Hash (SHA-256):
ef7797e13d3a75526946a3bcf00daec9fc9c9c4d51ddc7cc5df888f74dd434d1
Notice how no matter the input size, the hash is always the same length. Even changing a single character in the input drastically changes the hash. This property makes hashes perfect for security.
Properties of Cryptographic Hash Functions
Hash functions used in blockchain have special properties that make them secure:
- Deterministic : Same input always produces the same hash.
- Fixed Length Output : Regardless of input size, the hash length is fixed.
- Pre-image Resistance : Impossible to reverse-engineer the original input from the hash.
- Collision Resistance : Two different inputs should not produce the same hash.
- Avalanche Effect : A small change in input creates a completely different hash.
Common Hashing Algorithms Used in Blockchain
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit) – Used by Bitcoin. Produces 64-character hashes.
- Keccak-256 : Used by Ethereum for creating addresses and security.
- Scrypt & X11 : Used in various altcoins to provide efficiency and resistance against ASIC mining.
Each algorithm serves the same core purpose: protecting data integrity.
How Does Blockchain Use Hashes?
1. Linking Blocks Together
Each block in a blockchain contains:
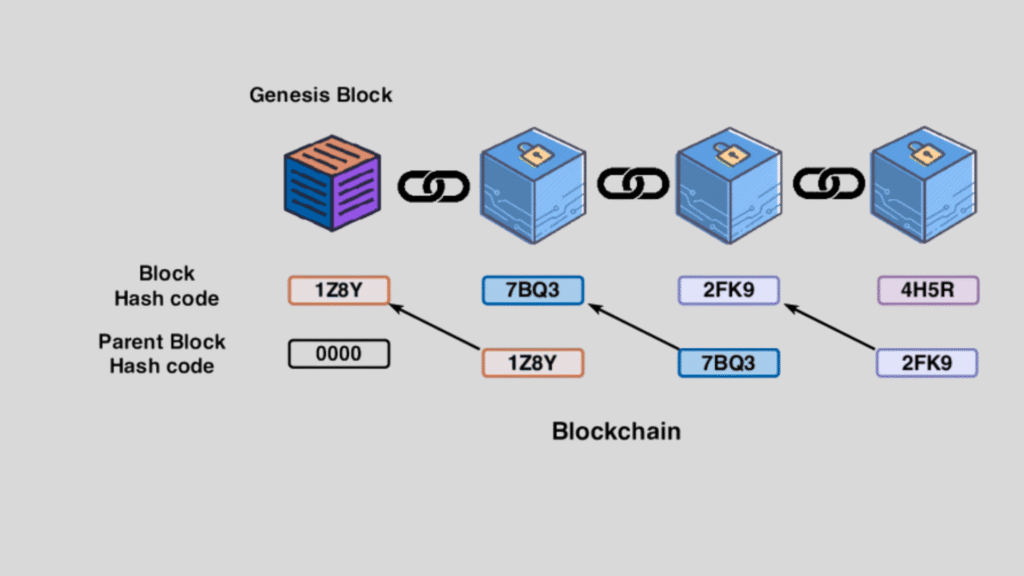
- Transaction data
- Timestamp
- Previous block’s hash
- Current block’s hash
The inclusion of the previous block’s hash creates a chain. If someone tries to alter data in one block, its hash changes, and all following blocks become invalid. This immutability is a cornerstone of blockchain security.
2. Proof of Work (Mining)
In Bitcoin and many other blockchains, miners solve a mathematical puzzle: finding a hash below a certain target.
- This requires computational power and time.
- Once solved, the block is added to the chain.
- Changing past data would require re-mining all blocks, which is nearly impossible.
Hashes, therefore, make blockchain resistant to tampering and fraud.
3. Digital Signatures and Verification
Blockchain also uses hashing to secure digital signatures:
- A private key signs the data.
- The hash of the data is encrypted.
- Other participants can use the public key to verify the authenticity.
This ensures that transactions are valid and not forged.
4. Merkle Trees
Blockchain transactions within a block are hashed into pairs, creating a binary tree called a Merkle Tree.
- The final root hash represents all transactions.
- If even one transaction changes, the root hash changes.
This allows efficient verification of large numbers of transactions.
Why Hashing Ensures Blockchain Security
1. Data Integrity
Hashes ensure that once data is written, it cannot be changed without detection.
2. Immutability
Each block’s hash depends on the previous block. Changing one block breaks the chain, making tampering obvious.
3. Consensus Verification
Nodes use hashes to agree on the validity of blocks, maintaining trust across decentralized systems.
4. Transparency & Trust
Public blockchains rely on hash-based security to build trust without intermediaries.
Real-World Applications of Hashing in Blockchain
- Cryptocurrencies : Every Bitcoin transaction is hashed for verification.
- Supply Chain : Companies use hashing to prove authenticity of goods.
- Healthcare : Patient records are hashed for tamper-proof security.
- Voting Systems : Each vote can be hashed to ensure it hasn’t been altered.
- NFTs : Unique digital assets use hashes to guarantee authenticity and ownership.
Advantages of Using Hashes in Blockchain
- Tamper-proof transactions
- High data security
- Efficient verification through Merkle Trees
- Protection against fraud
- Scalability in distributed systems
Challenges of Hashing in Blockchain
- High energy consumption in Proof of Work systems.
- Quantum computing threat (future quantum algorithms might break current hashes).
- Scalability issues with growing blockchain sizes.
- Complexity : Understanding cryptography is difficult for general users.
Future of Hashing in Blockchain
- Post-Quantum Hashing: Developing new algorithms resistant to quantum attacks.
- Greener Consensus: Moving from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake reduces hash computation energy.
- Integration with AI: Hashes may secure AI decision-making systems.
- Wider Adoption: Governments, businesses, and global organizations are testing blockchain secured by advanced hashing.
Conclusion
The security of blockchain technology rests heavily on hash functions. They provide immutability, protect data from tampering, and make decentralized trust possible. From Bitcoin mining to verifying digital signatures, hashing is at the heart of blockchain.
As blockchain grows into new industries finance, healthcare, governance the role of hashing will become even more critical. In the digital future, where trust is everything, hashing is the key that locks security into blockchain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a hash in blockchain?
A hash is a fixed-length output from a cryptographic function used to secure and verify blockchain data.
Q2. Why is hashing important for blockchain security?
Hashing ensures immutability, prevents tampering, and secures transactions in decentralized networks.
Q3. Which hashing algorithm does Bitcoin use?
Bitcoin uses SHA-256, a 256-bit secure hash algorithm.
Q4. Can a blockchain hash be reversed?
No. Hashes are one-way functions; the original data cannot be recovered from the hash.
Q5. What is a Merkle Tree in blockchain?
A Merkle Tree is a structure where hashes of transactions are combined, allowing efficient and secure verification.
Business
Great Western Buildings Lawsuit Explained

Legal disputes in the construction and manufacturing industry often raise important questions about business practices, contract obligations, and customer trust. One such case that has attracted attention is the Great Western Buildings lawsuit. While many people search for quick answers, the topic deserves a deeper explanation to understand what led to the lawsuit, its broader impact, and the lessons it offers for the construction and metal building industry.
This article explains the Great Western Buildings lawsuit, including its possible causes, effects on customers and the industry, and the key takeaways businesses and consumers should learn from it.
Understanding Great Western Buildings
Great Western Buildings is a company associated with the metal and steel building industry, a sector known for providing pre-engineered structures for agricultural, commercial, and industrial use. Companies in this space typically offer services such as:
- Steel building manufacturing
- Custom building design
- Delivery and installation support
- Long-term warranties and maintenance guidance
Like many construction-related businesses, Great Western Buildings operated in a competitive environment where contracts, timelines, and quality standards are critical.
What Is the Great Western Buildings Lawsuit?
The Great Western Buildings lawsuit refers to legal claims involving disputes over business practices, contractual obligations, or project execution. Lawsuits of this nature often arise when one or more parties believe that agreements were not honored or expectations were not met.
Although lawsuits can involve multiple claims and perspectives, they generally revolve around issues such as:
- Contract disputes
- Alleged construction defects
- Project delays
- Financial disagreements
- Warranty or service-related concerns
It is important to note that lawsuits do not automatically imply wrongdoing. They are part of the legal system’s process for resolving disputes between parties.
Common Causes Behind Construction Lawsuits
To understand the Great Western Buildings lawsuit more clearly, it helps to look at common causes of lawsuits in the construction and building industry.
1. Contractual Disputes
Contracts define scope, cost, materials, timelines, and responsibilities. Lawsuits often arise when:

- Terms are unclear
- Deadlines are missed
- Payment schedules are disputed
Even small ambiguities can lead to major legal disagreements.
2. Quality and Construction Standards
Customers may raise legal concerns if they believe:
- Materials were substandard
- Workmanship did not meet industry standards
- The finished structure differed from agreed specifications
Quality-related disputes are among the most frequent in construction litigation.
3. Delays and Project Management Issues
Construction projects are time-sensitive. Delays caused by:
- Supply chain disruptions
- Labor shortages
- Poor coordination
can result in financial losses, leading affected parties to seek legal remedies.
4. Warranty and Post-Construction Support
Many building companies offer warranties. Disputes can arise when:
- Repairs are delayed or denied
- Warranty terms are misunderstood
- Responsibilities are disputed
These issues often escalate when communication breaks down.
Impact of the Great Western Buildings Lawsuit
Impact on Customers
Customers involved in or affected by legal disputes may face:
- Project delays
- Financial uncertainty
- Difficulty reselling or refinancing properties
- Stress related to unresolved claims
Even customers not directly involved may become cautious when researching the company.
Impact on the Company
For businesses, lawsuits can lead to:
- Legal expenses
- Reputational challenges
- Operational disruptions
- Increased regulatory scrutiny
Public perception plays a major role, especially in industries that rely on trust and long-term client relationships.
Impact on the Construction Industry
High-profile lawsuits often influence the broader industry by:
- Encouraging stricter contract standards
- Improving transparency
- Raising awareness about compliance and quality control
While legal disputes are disruptive, they can also push industries toward better practices.
How Lawsuits Affect Brand Reputation
In the digital age, news about lawsuits spreads quickly. Search results, online reviews, and social media discussions can shape public opinion long before a case is resolved.
For construction companies, reputation matters because:
- Projects involve large financial investments
- Clients rely heavily on trust
- Referrals play a major role in growth
This is why many companies now invest heavily in legal compliance, customer communication, and dispute prevention.
Legal Perspective: Why Construction Lawsuits Are Complex
Construction lawsuits are often complex due to:
- Multiple parties (manufacturers, contractors, subcontractors, clients)
- Technical engineering details
- Long project timelines
- Overlapping responsibilities
Courts usually rely on contracts, expert testimony, and documentation to determine outcomes. This complexity means cases can take months or even years to resolve.
Lessons for Businesses from the Great Western Buildings Lawsuit
1. Clear and Detailed Contracts
Contracts should:
- Use plain language
- Clearly define responsibilities
- Outline dispute resolution methods
Clear contracts reduce misunderstandings and legal risks.
2. Strong Quality Control
Regular inspections, material verification, and documented processes help prevent quality-related disputes.
3. Transparent Communication
Many lawsuits escalate due to poor communication. Keeping clients informed about delays, changes, or challenges builds trust and reduces conflict.
4. Proper Documentation
Maintaining records of:
- Emails
- Change orders
- Inspections
- Payments
can be crucial if disputes arise.

Lessons for Customers and Buyers
Customers can also reduce risk by:
- Carefully reviewing contracts
- Asking questions before signing
- Keeping written records
- Understanding warranty terms
An informed customer is better prepared to handle potential issues.
Is a Lawsuit the End of a Company?
Not necessarily. Many companies:
- Resolve disputes
- Improve operations
- Rebuild trust
A lawsuit can be a turning point rather than an endpoint, depending on how a company responds.
The Bigger Picture: Industry Accountability
Cases like the Great Western Buildings lawsuit highlight the importance of:
- Ethical business practices
- Accountability
- Legal compliance
They remind both companies and customers that transparency and fairness are essential in long-term business success.
Final Thoughts
The Great Western Buildings lawsuit serves as an important example of how legal disputes can arise in the construction and metal building industry. While lawsuits are complex and often misunderstood, they offer valuable lessons about contracts, communication, quality, and trust.
For businesses, the case underscores the importance of strong operational standards and legal preparedness. For customers, it highlights the value of due diligence and informed decision-making. Ultimately, such cases push the industry toward higher standards and better practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What the Great Western Buildings lawsuit is about?
The Great Western Buildings lawsuit involves legal disputes related to contracts, project execution, quality concerns, or service issues commonly seen in the construction and metal building industry.
Whether a lawsuit means Great Western Buildings acted illegally?
A lawsuit does not automatically mean wrongdoing. It represents a legal claim or dispute, and responsibility is determined only after court decisions or settlements.
How construction lawsuits usually begin?
Construction lawsuits typically begin due to contract disagreements, project delays, quality or material concerns, payment disputes, or warranty-related issues.
How lawsuits can affect customers not directly involved?
Even customers not part of the lawsuit may experience indirect effects such as delayed projects, reduced confidence, or changes in company operations.
Whether construction lawsuits are common?
Yes, construction lawsuits are relatively common due to the complexity, cost, and long timelines involved in building projects.
What businesses can do to avoid similar lawsuits?
Businesses can reduce legal risks by using clear contracts, maintaining strong quality control, communicating transparently with clients, and keeping detailed documentation.
Whether customers should avoid companies involved in lawsuits?
Customers should research the situation carefully, review outcomes, and evaluate how the company addresses issues before making a decision.
Business
Finviz Explained: A Complete Guide to Stock Screening, Futures, and Market Analysis

In today’s fast-moving financial markets, having the right data at the right time can make all the difference. Traders and investors need tools that simplify complex market information and turn raw data into actionable insights. One such powerful platform is Finviz.
Finviz, short for Financial Visualizations, is widely used by traders, investors, and analysts to screen stocks, track futures, analyze market trends, and visualize financial data. Whether you are a beginner learning the basics or an experienced trader refining your strategy, Finviz offers tools that can significantly improve your decision-making.
This complete guide explains what Finviz is, how it works, and how to use its stock screening, futures data, and market analysis features effectively.
What Is Finviz?
Finviz is an online financial analysis platform designed to help users analyze stocks, futures, forex, and overall market performance using visual data and advanced filters. It aggregates information from multiple sources and presents it in a clean, easy-to-understand format.
The platform is best known for its:
- Powerful stock screener
- Interactive charts and heat maps
- Real-time futures and market data
- News aggregation and insider trading insights
Finviz is available in both free and paid (Finviz Elite) versions, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Why Finviz Is Popular Among Traders and Investors
Finviz has gained popularity because it combines simplicity with depth. Unlike many complex trading platforms, Finviz does not require software installation and works directly in a web browser.
Key reasons traders use Finviz include:
- Fast stock filtering using dozens of criteria
- Visual representation of market trends
- All-in-one dashboard for stocks, futures, and news
- Time-saving analysis tools
Whether your goal is day trading, swing trading, or long-term investing, Finviz helps you spot opportunities quickly.
Understanding the Finviz Stock Screener
The Finviz stock screener is the platform’s most powerful feature. It allows users to filter thousands of stocks based on technical, fundamental, and descriptive criteria.
1. Descriptive Filters
These filters help narrow down stocks by general characteristics such as:
- Market capitalization
- Sector and industry
- Country and exchange
- Index inclusion
This is useful if you want to focus on specific markets, like U.S. tech stocks or small-cap companies.
2. Fundamental Filters
Fundamental analysis focuses on a company’s financial health. Finviz provides filters such as:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio
- Earnings growth
- Revenue growth
- Dividend yield
- Debt-to-equity ratio
Long-term investors use these filters to find undervalued or fundamentally strong stocks.
3. Technical Filters
Technical traders rely heavily on price action and trends. Finviz offers filters like:
- Moving averages
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- Pattern recognition
- Support and resistance levels
- Volume and volatility
These filters are ideal for day traders and swing traders looking for momentum or breakout setups.
4. Using Presets and Custom Screens
Finviz provides built-in presets such as:
- Oversold stocks
- Top gainers
- New highs or lows
You can also save custom screeners, allowing you to reuse your strategy daily without rebuilding filters.
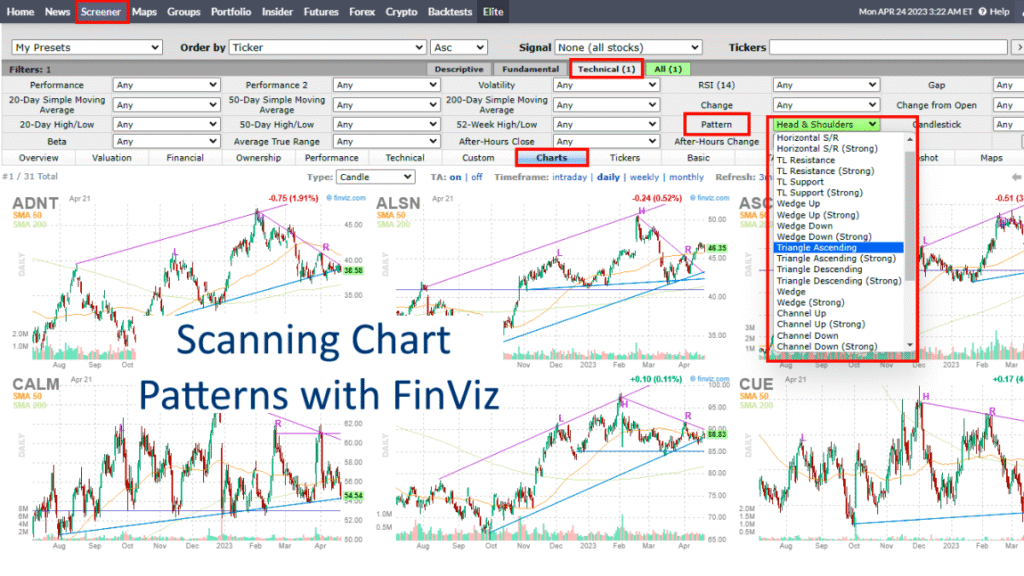
Finviz Charts and Visual Tools
Finviz stands out because of its visual approach to market data.
Interactive Stock Charts
Each stock has an interactive chart showing:
- Price movement
- Volume
- Technical indicators
- Pattern highlights
These charts help traders quickly identify trends without switching platforms.
Market Heat Maps
The heat map feature visually displays market performance by:
- Sector
- Industry
- Individual stocks
Green indicates gains, red indicates losses, and size represents market capitalization. This tool is excellent for spotting sector rotation and market sentiment at a glance.
Performance Maps
Performance maps show how stocks or sectors have performed over specific time frames, helping investors understand short-term and long-term trends.
Futures Data on Finviz
Finviz also provides valuable insights into futures markets, which are essential for understanding broader market direction.
Available Futures Markets
Finviz tracks major futures such as:
- S&P 500 futures
- Nasdaq futures
- Dow Jones futures
- Crude oil
- Gold and silver
- Agricultural commodities
This data is crucial for traders who want to anticipate market openings and global trends.
Why Futures Data Matters
Futures often move before stock markets open. By analyzing futures:
- Traders can predict market sentiment
- Investors can prepare for volatility
- Day traders can plan entries and exits
Finviz displays futures data in a simple format, making it accessible even for beginners.
Market News and Insider Trading Insights
Financial News Aggregation
Finviz pulls news from trusted financial sources and links headlines directly to relevant stocks. This allows users to:
- Stay updated on market-moving events
- React quickly to earnings or announcements
- Understand why a stock is moving
Insider Trading Data
One unique feature of Finviz is its insider trading section, which tracks:
- Insider buys and sells
- Transaction sizes
- Timing patterns
Finviz Free vs Finviz Elite
Free Version Features
The free version includes:
- Delayed quotes
- Basic stock screener
- Heat maps
- Market news
It’s perfect for beginners or casual investors.
Finviz Elite Features
Finviz Elite unlocks advanced tools such as:
- Real-time data
- Advanced charting
- Backtesting capabilities
- Exportable screening results
- No advertisements
Active traders often upgrade to Elite for speed, accuracy, and deeper analysis.
Who Should Use Finviz?
Finviz is suitable for a wide range of users:
- Beginners learning stock market basics
- Day traders looking for momentum stocks
- Swing traders identifying technical setups
- Long-term investors analyzing fundamentals
- Market analysts tracking overall trends
Its flexibility makes it a valuable tool regardless of trading style.
Pros and Cons of Finviz
Pros
- Easy-to-use interface
- Powerful stock screening
- Visual market analysis
- Free version available
- Covers stocks, futures, and news
Cons
- Limited backtesting in free version
- Not a trading execution platform
- Some data is delayed without Elite
Despite a few limitations, Finviz remains one of the most efficient market research tools available online.
Tips for Using Finviz Effectively
- Combine technical and fundamental filters for better results
- Use heat maps daily to track sector strength
- Save custom screeners for consistency
- Cross-check signals with other tools
- Avoid over-filtering, which can limit opportunities
With practice, Finviz can become a daily habit that improves your trading discipline.

Final Thoughts
Finviz is more than just a stock screener. It is a complete market analysis platform that brings together stock screening, futures data, charts, news, and visual insights in one place. Its intuitive design and powerful features make it suitable for both beginners and professionals.
If you want to save time, reduce noise, and make smarter market decisions, Finviz is a tool worth adding to your trading routine. Whether you use the free version or upgrade to Elite, the platform offers valuable insights that can help you stay ahead in today’s competitive financial markets.
Business
Business Software Gonzay Com: Smart Solutions for Technology, Health & Apps

In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are increasingly relying on smart software solutions to stay competitive, efficient, and customer-focused. Platforms like Business Software Gonzay Com are gaining attention for offering insights and solutions across technology, health software, and app development. Whether you are a startup founder, a small business owner, or a tech enthusiast, understanding how such platforms support modern industries can help you make informed decisions.
This article explores Business Software Gonzay Com, its focus areas, benefits, and how it contributes to the evolving digital ecosystem.
What Is Business Software Gonzay Com?
It appears to be an online platform focused on business-oriented software solutions, technology trends, digital health innovations, and application development. The platform aims to bridge the gap between complex technology and real-world business needs by offering simplified explanations, tools, and insights.
Its core purpose is to help businesses and individuals understand how software can improve operations, enhance productivity, and support innovation in multiple sectors.
Core Areas Covered by Business Software Gonzay Com
Business Software Gonzay Com mainly focuses on three growing domains:
- Technology Solutions
- Health-Related Software
- App and Software Development
Let’s explore each in detail.
1. Technology Solutions for Modern Businesses
Digital Transformation Support
Technology is the backbone of modern business success. Business Software Gonzay Com emphasizes digital transformation, helping companies move from manual systems to automated, cloud-based, and AI-driven solutions.
Key areas include:
- Cloud computing
- Business automation tools
- Data analytics
- Cybersecurity awareness
- Artificial intelligence integration
These technologies help businesses reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve decision-making.
Business Management Software
Business Software Gonzay Com highlights tools designed for:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Accounting and finance software
- Inventory and supply chain management
Such software solutions allow organizations to manage daily operations more effectively and maintain long-term growth.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
With increasing cyber threats, data security is critical. The platform stresses:
- Secure software practices
- Data encryption
- Compliance awareness
- Risk management strategies
Businesses that prioritize cybersecurity not only protect their data but also build customer trust.
2. Health Technology and Software Solutions
The Rise of Digital Health
Health technology has transformed how medical services are delivered. Business Software Gonzay Com covers the growing field of health software, which includes digital tools designed to improve patient care, healthcare management, and medical data handling.
Healthcare Software Applications
Common health-related software solutions discussed include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- Telemedicine platforms
- Patient management systems
- Health monitoring applications
- Medical billing software
These tools help healthcare providers streamline operations and deliver better patient outcomes.
Benefits of Health Software
Health technology solutions provide:
- Faster access to patient data
- Improved accuracy in diagnosis
- Better communication between patients and doctors
- Cost reduction in healthcare operations
- Remote healthcare access
It emphasizes how digital health software supports both healthcare providers and patients in a modern, connected world.
Compliance and Data Privacy in Health Tech
Healthcare software must comply with strict data protection rules. The platform highlights the importance of:
- Secure patient data handling
- Ethical software development
- Privacy-focused system design
This is essential for maintaining trust and legal compliance in the healthcare industry.
3. App Development and Software Innovation
Importance of App Development Today
Mobile and web applications are now essential for business success. It focuses heavily on app development, helping users understand how apps drive engagement, sales, and brand visibility.
Types of Apps Covered
The platform discusses various app categories, including:
- Business productivity apps
- Health and fitness apps
- E-commerce applications
- Educational apps
- Custom enterprise solutions
Each app type serves specific business goals and user needs.
App Development Process Explained
It breaks down the app development lifecycle into simple stages:
- Idea and planning
- UI/UX design
- Front-end and back-end development
- Testing and debugging
- Deployment and maintenance
Understanding this process helps businesses plan their digital products more effectively.
Technologies Used in App Development
Common technologies discussed include:
- Programming languages like Java, Python, and JavaScript
- Frameworks for mobile and web apps
- Cloud-based app hosting
- API integration
- AI and machine learning features
These technologies enable scalable and future-ready applications.
Benefits
Easy-to-Understand Information
One major advantage of Business Software Gonzay Com is its focus on simplifying complex topics. This makes it useful for:
- Non-technical business owners
- Beginners in software development
- Entrepreneurs exploring digital tools
Multi-Industry Approach
By covering technology, health, and app development together, the platform provides a holistic view of how software impacts different industries.
Business Growth Support
The platform helps businesses:
- Identify suitable software solutions
- Understand digital trends
- Make informed technology investments
- Improve efficiency and scalability
Knowledge for Future Planning
With technology evolving rapidly, businesses must stay informed. Business Software Gonzay Com helps users:
- Prepare for digital innovation
- Adopt emerging technologies
- Stay competitive in changing markets
Why Technology, Health, and App Development Are Connected
These three areas are deeply interconnected:
- Technology enables innovation
- Health software improves quality of life
- App development delivers solutions directly to users
It highlights how combining these domains leads to smarter, more impactful digital products.
For example:
- Health apps rely on advanced technology
- Business software uses app platforms
- Data analytics improves healthcare decisions
This integrated approach reflects the future of digital solutions.
Who Can Benefit from Business Software Gonzay Com?
The platform is useful for:
- Small and medium business owners
- Healthcare professionals
- Startup founders
- Software developers
- IT managers
- Students learning technology concepts
Anyone interested in understanding how software drives modern industries can benefit.
Challenges and Considerations
While business software offers many benefits, Business Software Gonzay Com also emphasizes challenges such as:
- High development costs
- Data security risks
- User adoption issues
- Maintenance and updates
Understanding these challenges helps businesses plan better and avoid common mistakes.
The Future of Business Software and Digital Innovation
Looking ahead, Business Software Gonzay Com aligns with future trends such as:
- Artificial intelligence in healthcare
- Automation in business operations
- Cloud-based app ecosystems
- Personalized digital experiences
- Remote and mobile-first solutions
These trends indicate that software will continue to play a crucial role in shaping global industries.
Final Thoughts
Business Software Gonzay Com represents a modern approach to understanding and leveraging software in business, healthcare, and app development. By focusing on technology education, health innovation, and digital product development, the platform supports businesses and individuals navigating the digital age.
As industries become more technology-driven, platforms like Business Software Gonzay Com help simplify complex concepts and empower smarter decisions. Whether you’re planning to build an app, invest in health software, or modernize your business operations, understanding these interconnected domains is key to long-term success.
FAQ
What is Business Software Gonzay Com?
Business Software Gonzay Com is a platform that focuses on business technology, health software solutions, and app development insights.
Who can use Business Software Gonzay Com?
Entrepreneurs, startups, healthcare providers, developers, and business owners can benefit from its software-related content.
Does Business Software Gonzay Com cover health technology?
Yes, it highlights digital health tools such as telemedicine apps, patient management systems, and healthcare software solutions.
Why is app development important for businesses?
App development helps businesses improve customer engagement, streamline operations, and expand their digital presence.
Is Business Software Gonzay Com suitable for small businesses?
Yes, it provides easy-to-understand information useful for startups and small businesses exploring digital tools.
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoWhy ’90s Fashion Still Dominates Today’s Style Scene
-

 Fashion6 months ago
Fashion6 months agoTop Fashion Trends to Follow in August 2025
-

 How-to Guides6 months ago
How-to Guides6 months agoHow to Restore Pantone Colors in New Illustrator Versions (2026 Guide)
-

 Politics6 months ago
Politics6 months agoReddit Politics: A Deep Dive into Online Political Discourse
-

 How-To Tutorials & Troubleshooting6 months ago
How-To Tutorials & Troubleshooting6 months agoHow to Screenshot on Mac: The Complete 2025 Guide






